
In our data-driven world, storage infrastructure is significantly more than just a place to keep files; it’s the bedrock upon which digital transformation rests. Despite this, traditional storage solutions often fail to meet the demands of modern businesses. Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) offers a new paradigm for data management.
ODF: More Than Storage, A Strategic Asset
Open Data Foundation (ODF) is a cloud-native software-defined storage platform engineered to tackle multifaceted data challenges. ODF goes beyond traditional storage solutions by transforming data into a strategic asset, empowering organizations to accelerate their digital transformation journeys. ODF delivers a comprehensive suite of capabilities designed to streamline data management, enhance agility, and unlock the full potential of your data:
- Unified Storage: Combines block, file, and object storage into a single platform, simplifying data management.
- Scalability: Seamlessly scales storage resources to meet evolving demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Resiliency: Ensures data integrity and availability through advanced replication, erasure coding, and disaster recovery techniques.
- Multi-Cloud Integration: Enables seamless integration with major public cloud providers, facilitating hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
- Data Services: Enhances data utilization with built-in features like data tiering, compression, deduplication, and encryption.
- Kubernetes-Native: Leverages Kubernetes for container orchestration, enabling efficient deployment and management of cloud-native applications.
- Open Source: Built on open standards and open-source technologies, fostering innovation and avoiding vendor lock-in.
The ODF Advantage: What Sets It Apart
ODF is a strategic investment that empowers a digital transformation:
- Streamlined Operations: Simplify data management with a single platform that handles all your storage needs.
- Accelerated Innovation: Quickly provision storage resources for new projects and applications, reducing time-to-market.
- Enhanced Data Protection: Safeguard your data with enterprise-grade security and resilience features.
- Improved Agility: Respond to changing business needs with a scalable, flexible storage solution.
ODF in Action: Unleashing the Power of Your Data
Imagine a world where your data is readily available, easily accessible, and securely managed. With ODF, that world becomes a reality. Here’s how organizations are leveraging ODF to drive their digital transformation:
- Modernizing Legacy Systems: ODF bridges traditional and cloud-native architectures, enabling a smooth transition to a modern data platform.
- Enabling Cloud-Native Applications: ODF seamlessly integrates with Kubernetes and containers, providing the ideal foundation for cloud-native development and deployment.
- Unifying Data Silos: Break down data barriers and create a unified view of your information assets, enabling better decision-making and collaboration.
Your Data, Your Way
ODF offers flexible deployment options to fit your specific environment and requirements:
- On-Premises: Leverage your existing infrastructure to build a private cloud storage solution.
- Hybrid Cloud: Seamlessly integrates on-premises and cloud storage for maximum flexibility and cost-efficiency.
- Multi-Cloud: Manage data across multiple cloud providers with a unified interface and consistent experience.
Under the Hood: ODF’s Architectural Blueprint
ODF operates like a well-coordinated team, with each component playing a vital role:
- OCS Operator: The orchestrator oversees the ODF operation and ensures all components work together seamlessly.
- Rook-Ceph Operator: This role manages the underlying Ceph storage cluster, which provides the core block, file, and object storage capabilities.
- NooBaa Operator: Handles multi-cloud object storage, allowing you to manage and access your data across different cloud providers with a unified interface.
The following diagram (Figure 1) illustrates a simplified architecture of Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation and the interaction between its various components.
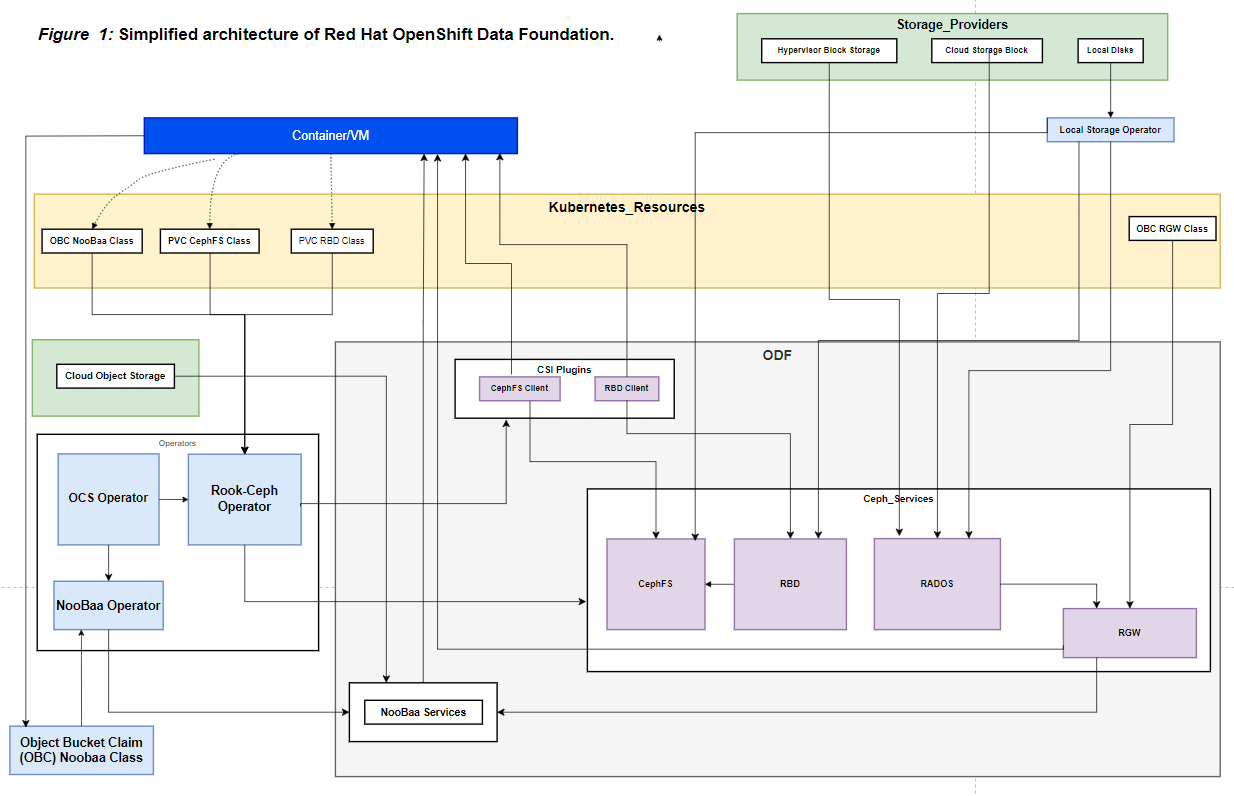
Fig 1. Interaction Flow:
- Storage Providers (Hypervisor Block Storage, Cloud Storage Block, and Local Disks) feed into the Local Storage Operator, which then integrates these resources into the Ceph Services.
- Ceph Services (RADOS, RBD, CephFS, RGW) provide the core storage functionalities, with RBD and CephFS consumed using OS system calls.
- NooBaa Services offer multi-cloud object storage and interact with both Ceph Services and Cloud Object Storage.
- CSI Plugins (RBD Client and CephFS Client) facilitate storage communication between Containers/VMs and the underlying storage systems.
- Operators (OCS Operator, Rook-Ceph Operator, and NooBaa Operator) manage and orchestrate the deployment and operation of these storage services.
- Kubernetes Resources (Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) for RBD and CephFS Classes, and Object Bucket Claims (OBCs) for NooBaa and RGW Classes) allow applications to request and utilize the storage services provided by OpenShift Data Foundation.
Objective Assessment: ODF vs. the Competition
To understand ODF’s position in the market, let’s compare it against other leading software-defined storage solutions using key criteria:
| Feature | Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) | VMware vSAN | Portworx by Pure Storage | StorageOS | Longhorn |
| Kubernetes Integration | Native, seamless integration | Integrated with VMware Tanzu | Native integration with Kubernetes | Native, purpose-built for Kubernetes | Native, designed for Kubernetes |
| Feature Set | Comprehensive (block, file, object) | Supports block and file storage | Advanced data management and security features | Enterprise-grade features (snapshot, replication) | Basic storage features |
| Performance | Excellent, optimized for Ceph | High performance with all-flash storage | High performance, scalable | Good performance for most workloads | Good performance for lightweight workloads |
| Ease of Use | Simplified with operator framework | Moderate, requires VMware ecosystem knowledge | User-friendly with comprehensive CLI and GUI | Easy to deploy and manage | Simple installation and management |
| Cost | Varies based on deployment (commercial support with enterprise features) | Premium pricing | Enterprise pricing | Flexible, depends on deployment size | Open Source, free to use |
| Multi-Cloud Support | Yes, native integration | Limited to VMware Cloud | Supports multiple cloud providers | Limited, primarily on-premises | Limited, primarily on-premises |
Overall Assessment: ODF stands out for its native Kubernetes integration, comprehensive feature set, and strong performance. While it may have higher upfront costs than some open-source alternatives, its simplified management and enterprise-grade features make it an ideal solution for businesses seeking a reliable, scalable, and cloud-native storage open-source solution.
Building Your Digital Future on ODF
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) is central to achieving a contemporary, high-performance, data-centric architecture. Its seamless integration with Kubernetes and support for block, file, and object storage types make it a versatile solution for modern data management needs. ODF’s scalability ensures it grows with your organization, delivering consistent performance and reliable data protection. By adopting ODF, organizations can streamline operations, improve data accessibility, and foster innovation, driving significant transformation and growth to their competitive advantage.
References
- Ceph Storage Interface. “Ceph CSI.” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://github.com/ceph/ceph-csi/.
- Ceph. “Ceph Glossary.” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/glossary/.
- Noobaa. “Noobaa Git Repo.” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://github.com/noobaa/.
- Red Hat. “OpenShift Container Storage Operator (OCS Operator).” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://docs.redhat.com/en/documentation/red_hat_openshift_container_storage/4.8/html/red_hat_openshift_container_storage_architecture/openshift_container_storage_operators/.
- Red Hat. “OpenShift Data Foundation Datasheet.” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/openshift-data-foundation-datasheet.
- Red Hat Developers. “Best Practices for OpenShift Data Foundation Disaster Recovery Resource Planning.” Accessed June 20, 2024. https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2024/02/22/best-practices-openshift-data-foundation-disaster-recovery-resource-planning.
- Red Hat. “Add Capabilities to Enterprise Deployments Datasheet.” Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/add-capabilities-enterprise-deployments-datasheet.
- Red Hat. “OpenShift Data Foundation Detail.” Accessed June 16, 2024. https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/openshift-data-foundation-detail.
- SelectHub. “OpenShift Data Foundation.” Accessed June 14, 2024. https://www.selecthub.com/p/data-governance-tools/openshift-data-foundation/.
- VMware. “VMware vSAN Documentation.” Accessed June 22, 2024. https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSAN/index.html.
- VMware. “VMware vSAN Product Page.” Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.vmware.com/products/vsan.html.
- Pure Storage. “Portworx Documentation.” Accessed June 20, 2024. https://docs.portworx.com/.
- Pure Storage. “Portworx Product Page.” Accessed June 16, 2024. https://portworx.com/.
- StorageOS. “StorageOS Product Page.” Accessed June 15, 2024. https://storageos.com/.
- StorageOS. “StorageOS GitHub Repository.” Accessed June 12, 2024. https://github.com/storageos.
- Longhorn. “Longhorn Product Page.” Accessed June 14, 2024. https://longhorn.io/.
- Longhorn. “Longhorn GitHub Repository.” Accessed June 10, 2024. https://github.com/longhorn/longhorn.