
Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Security
Due to the increasing use of distributed cloud architectures, managing security across multi-cloud and hybrid environments presents a significant challenge. IBM Security and Compliance Center (SCC) offers a unified approach to risk management, security, and compliance, equipping organizations with centralized tools for proactive threat detection and resilient cloud security.
The Multi-Cloud Security Imperative
Challenges of Securing Diverse Cloud Environments
As organizations increasingly adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud infrastructures, they face significant challenges in maintaining consistent security across diverse environments. Managing security across multiple cloud platforms (e.g., IBM Cloud, AWS, Azure, GCP) alongside data centers and on-premises systems creates a complex environment that requires centralized security management.
Dynamic Nature of Cloud Services: Traditional security methods often fail to address cloud environments’ dynamic nature, resulting in misconfigurations and compliance gaps. Static security solutions struggle to keep up with the rapidly evolving cloud landscape, leading to vulnerabilities and other security issues.
Shared Responsibility Model: In cloud environments, security responsibilities are divided between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer. CSPs secure the infrastructure, while customers are responsible for their data, applications, and user access. This model can result in security gaps and misaligned controls without effective management.
Fragmented Cloud Ecosystem: Using multiple cloud providers further complicates security management. Each cloud platform has its tools, configurations, and protocols, leading to inconsistent security practices and difficulty maintaining a unified security posture.
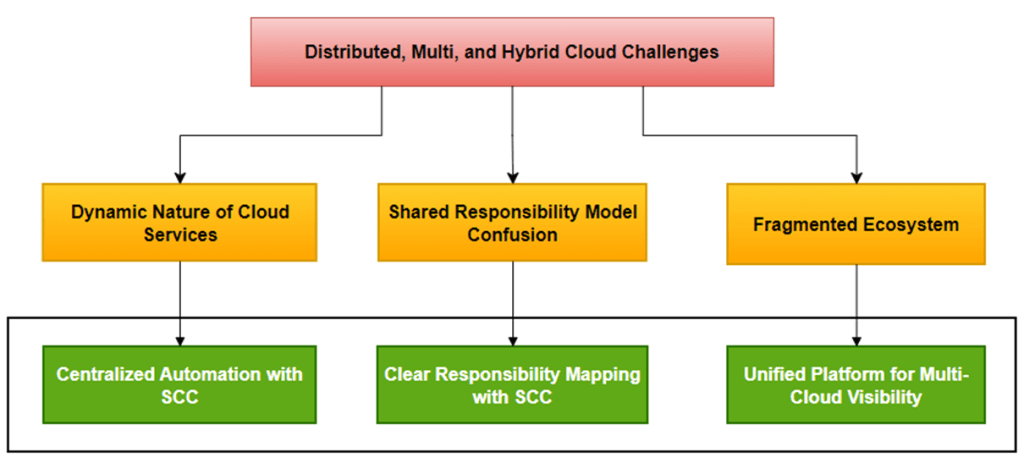
Figure 1 shows how IBM SCC addresses multi-cloud security challenges, offering unified visibility for dynamic environments, consistent policy enforcement across platforms, and streamlined compliance for fragmented ecosystems.
Organizations need a cohesive strategy that combines all security efforts to tackle these complex challenges effectively. The fragmented nature of managing multiple cloud environments, the confusion around shared responsibilities, and the dynamic landscape of cloud services all point to one clear solution: centralized security management. A centralized approach provides the control and consistency that traditional, disjointed security measures lack by unifying visibility, standardizing policies, and streamlining compliance across diverse environments. This is where the IBM Security and Compliance Center becomes invaluable, offering a single, integrated platform to meet the demands of a modern multi-cloud security landscape.
The Need for Centralized Security Management
Organizations need a unified, centralized approach to security management to address the challenges of multi-cloud and hybrid environments. Centralizing security management provides essential benefits such as:
- Unified Visibility and Control: A single pane of glass for monitoring and managing security across all cloud platforms, enabling quick identification and response to threats, regardless of origin.
- Consistent Policy Enforcement: Uniform security policies across environments ensure a robust security posture and adherence to regulatory standards, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
- Streamlined Compliance and Risk Management: Centralized control helps meet compliance requirements (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, NIST) more efficiently while facilitating effective risk assessment and prioritization across the entire infrastructure.
- Automated Operations and Cost Efficiency: Centralized management supports the automation of security processes, reducing manual workloads and operational costs while enabling rapid responses to dynamic cloud changes.
The unified approach centralizes security controls and optimizes the entire risk management lifecycle, which is increasingly essential as organizations expand across multiple clouds.
Bridging the Multi-Cloud Security Gap
IBM Security and Compliance Center is designed to tackle the complex security challenges of managing multi-cloud and hybrid environments. It offers a unified approach to risk management, compliance automation, and security across diverse cloud infrastructures.
Core Components
IBM Security and Compliance Center comprises several core components that work together to provide a comprehensive security solution:
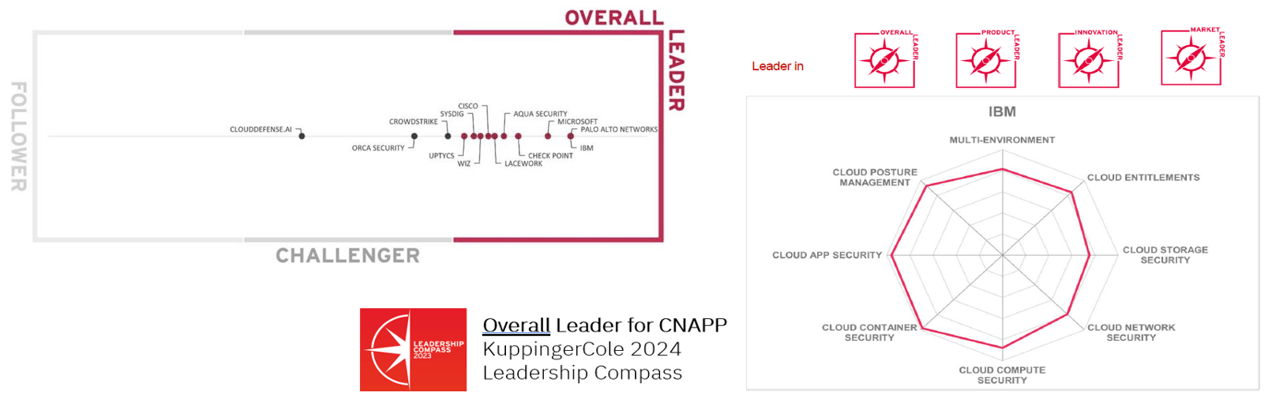
Figure 2: 2024 KuppingerCole Leadership Compass for CNAPP This figure highlights IBM SCC’s overall leader in the 2024 KuppingerCole CNAPP (Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform) Leadership Compass report. The radar chart illustrates IBM’s leadership across multiple categories, including Cloud Posture Management, Cloud Entitlements, Cloud Storage Security, Cloud Network Security, Cloud Compute Security, Cloud Container Security, Cloud App Security, and Multi-Environment capabilities. IBM ranks highly in product innovation, overall functionality, market presence, and leadership in various cloud security dimensions, reflecting its comprehensive capabilities and strategic vision in the cloud-native security domain.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP): CNAPP provides end-to-end security for cloud-native applications, integrating protection across workloads, containers, and serverless functions. It focuses on runtime monitoring, threat detection, and policy enforcement to ensure compliance and secure modern application architectures.
Compliance Automation: This product supports predefined frameworks (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and NIST) and enables custom creation, simplifying compliance efforts and reducing audit workload across hybrid environments.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Provides visibility into cloud assets, identities, and misconfigurations. CSPM continuously monitors and automates remediation to reduce risks and ensure compliance, maintaining a strong security posture across hybrid environments.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP): CWPP protects workloads across cloud-native and traditional environments, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. It offers host-level security, runtime protection, and workload-specific compliance monitoring to safeguard against vulnerabilities.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) manages cloud identities and permissions to detect security risks related to user access. It enforces the least privileges to minimize the attack surface.
Unified Risk Management: This provides a unified dashboard for monitoring security risks. It offers detailed reports on misconfigurations, compliance violations, and remediation actions to help organizations make informed decisions.
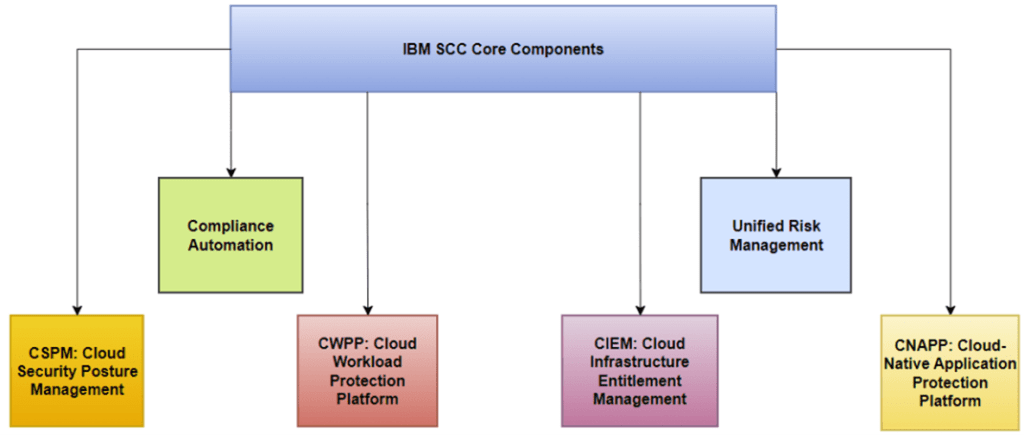
Figure 3 illustrates how the core components of IBM SCC—CSPM, CNAPP, CWPP, CIEM, Unified Risk Management, and Compliance Automation—contribute to a unified security approach, ensuring consistent policy enforcement and comprehensive resilience across hybrid environments.
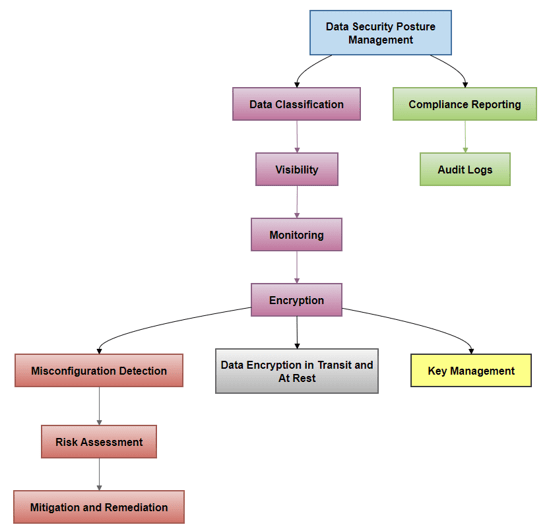
Figure 4, Data Security Posture Management Workflow, shows the data security posture management workflow within IBM SCC. The process starts with data classification and visibility, followed by monitoring for any misconfigurations. Risks are then assessed, leading to mitigation and remediation actions to maintain data security.
Data Security in IBM SCC
IBM Security and Compliance Center (SCC) provides several features to ensure data security across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. These features focus on protecting data at rest, in transit, and during processing, ensuring regulatory compliance and a robust data posture. Key data security features include:
- Data Security Broker
- Tokenization and Encryption: SCC integrates with IBM’s Data Security Broker, which provides tokenization and encryption capabilities. This allows organizations to replace sensitive data with tokens or encrypt data before storing it, ensuring that sensitive information is protected during storage or transfer.
- Access Control: The Data Security Broker supports managing and restricting access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive information.
- Encryption and Key Management
- FIPS 140-2 Level 4 HSM Integration: SCC integrates with IBM’s Hyperprotect Services to provide encryption using FIPS 140-2 Level 4 hardware security modules (HSM), ensuring secure storage and management of encryption keys.
- Cloud-Native Encryption: SCC leverages native encryption mechanisms within each cloud platform to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Compliance Automation Related to Data Protection
- Automated Compliance Checks for Data Security Standards: SCC continuously monitors and assesses data-related configurations against GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA standards.
- Audit Trail for Data Security Compliance: SCC generates detailed logs and audit trails for all data security-related activities, helping organizations prove adherence to regulatory standards.
- Access Control and Entitlement Management
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM): SCC enforces the least privileged access for cloud data to minimize the attack surface.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): SCC limits data access based on user roles, ensuring secure handling of sensitive data.
- Data Security Posture Management
- Data Classification and Visibility: SCC identifies where sensitive data resides across environments and applies appropriate security controls.
- Misconfiguration Detection: SCC monitors data storage configurations, such as cloud storage buckets, flagging any risks that could compromise data security.
- Data Protection in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
- Integrated Workload Protection: SCC provides runtime security for databases, applications, and storage systems handling sensitive data during processing.
- Network Security for Data Protection: SCC monitors data flows for anomalies to protect data in transit.
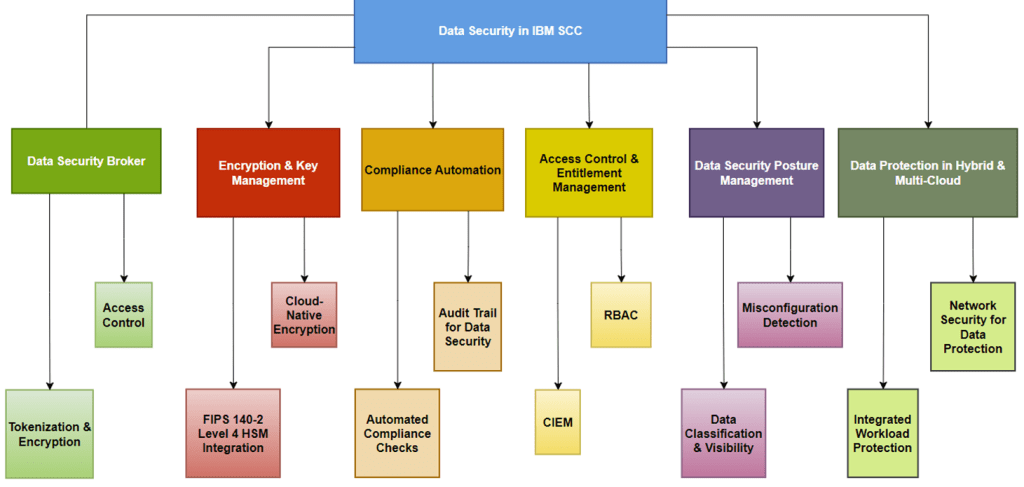
Figure 5 illustrates Data Security in IBM SCC, highlighting key focus areas such as Data Security Broker, Encryption and Key Management, Compliance Automation, Access Control and entitlement Management, Data Security Posture Management, and Data Protection in Hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Each component is critical in ensuring data security at every stage—whether at rest, in transit, or during processing—across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Integration Capabilities with Major Cloud Providers
IBM Security and Compliance Center integrates with major cloud providers, allowing centralized security management across multi-cloud and hybrid infrastructures:
- AWS Integration: Provides visibility into EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and other AWS resources, monitoring configurations and applying security policies consistently across AWS environments.
- Azure Integration: Monitors and secures resources like virtual machines, storage accounts, and networking components within Azure environments.
- IBM Cloud Integration: Delivers comprehensive security and compliance management for workloads on IBM’s cloud infrastructure, ensuring deep integration with IBM Cloud services.
- On-Premises Integration: Extends capabilities to on-premises environments, allowing organizations to maintain unified security across hybrid infrastructures.
- Multi-Cloud Visibility: By integrating with multiple cloud providers, the solution offers a consolidated view of security risks, compliance status, and resource configurations, helping identify and address security gaps across diverse cloud platforms.
- API-Driven Architecture: The API-driven approach facilitates seamless integration with existing IT and security tools, allowing organizations to extend capabilities and integrate security into their current workflows.
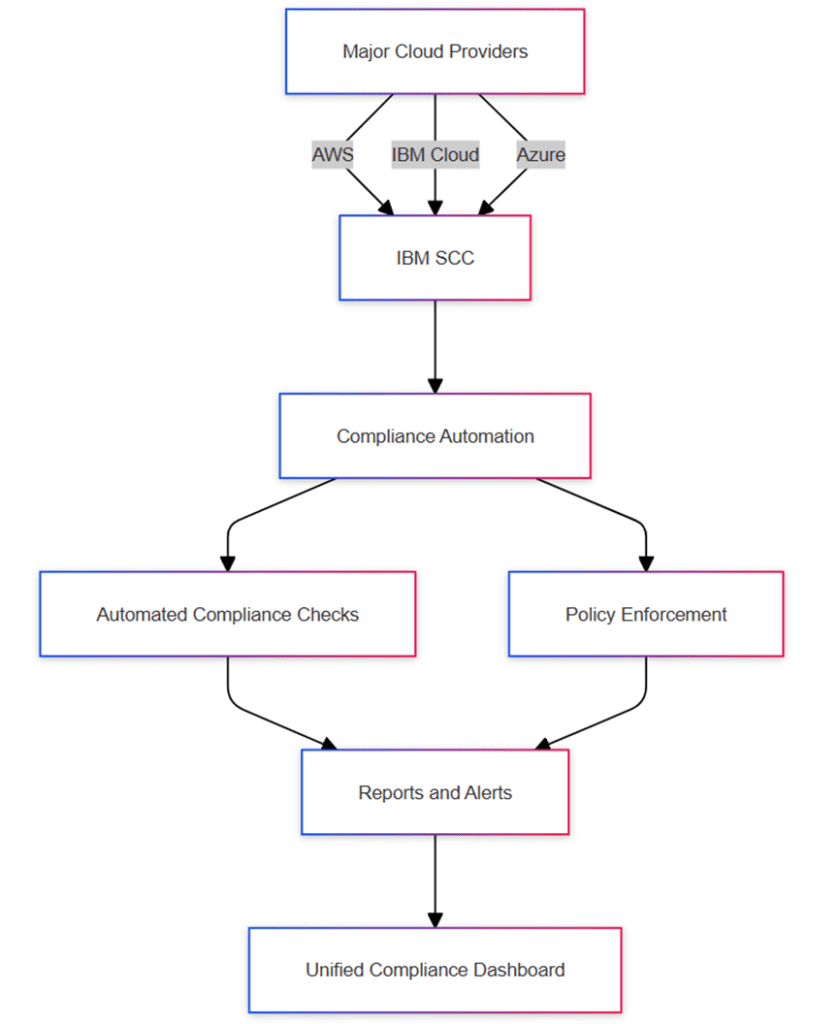
Figure 6, Cloud Integration and Compliance Automation Workflow, shows how IBM SCC integrates with major cloud providers, such as AWS, IBM Cloud, and Azure, to funnel data through a compliance automation process. SCC collects data and then performs automated compliance checks and policy enforcement, with the results presented in a unified compliance dashboard.
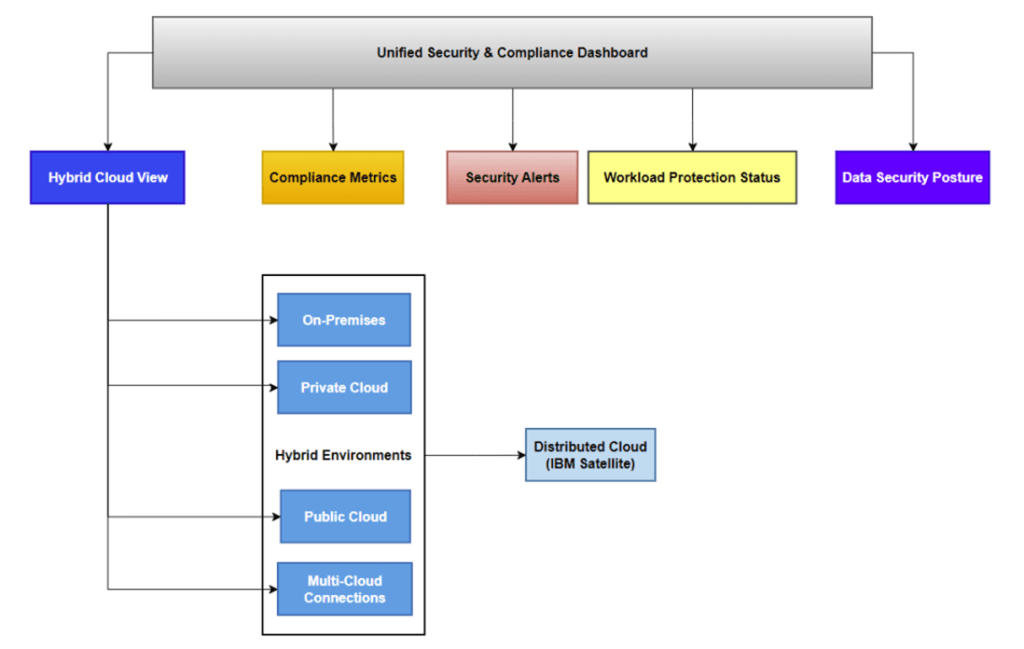
Figure 7 illustrates the capabilities of the IBM SCC Unified Security & Compliance Dashboard. It integrates multiple views, such as Hybrid Cloud View, Compliance Metrics, Security Alerts, Workload Protection Status, and Data Security Posture, across various environments, including on-premises, private, public, and distributed cloud (IBM Satellite). The dashboard enables centralized visibility and management, ensuring consistent security and compliance throughout cloud and on-premises configurations.
Collectors in IBM SCC
Collectors in IBM SCC are essential in gathering data for monitoring, compliance, and security enforcement across cloud environments. There are two types of collectors, each serving specific use cases:
- IBM-Managed Collectors
- Automated Collection: IBM-managed collectors are automatically deployed, configured, and updated by IBM, reducing operational burden.
- Best for Common Compliance Scenarios: These collectors are ideal for standard compliance requirements, providing consistent data for compliance checks and security analysis.
- Customer-Managed Collectors
- Customization Flexibility: Customer-managed collectors can be customized based on unique requirements.
- Deployed Based on Specific Needs: These collectors are deployed, configured, and managed by the customer, allowing more flexibility for particular security and monitoring needs.
Key Features of Collectors:
- Scalable Data Collection: Both collector types can be deployed at scale to cover large cloud and hybrid infrastructures.
- Real-Time Data Gathering: Collectors enable continuous data gathering, ensuring that SCC has up-to-date information for compliance and threat detection.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Collectors integrate seamlessly with cloud environments and existing on-prem systems to gather data comprehensively.
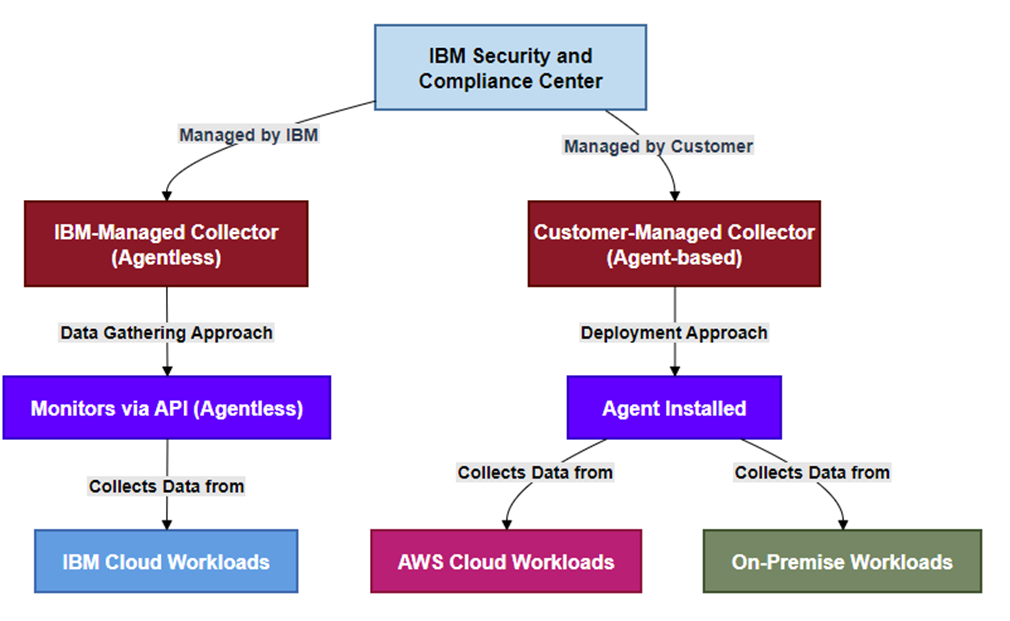
Figure 8 illustrates the two types of data collectors used by the IBM Security and Compliance Center (SCC): IBM-managed collectors (agentless) and customer-managed collectors (agent-based). IBM-managed collectors are deployed and managed by IBM, using APIs for data gathering from IBM Cloud Workloads. On the other hand, customer-managed collectors require agent installation by the customer and are used to gather data from AWS Cloud Workloads and On-Premises Workloads. Each type of collector serves a distinct purpose, providing flexibility in data gathering and monitoring based on deployment needs.
Continuous Compliance and Risk Management
The IBM Security and Compliance Center provides a robust approach to continuous compliance and risk management across hybrid multi-cloud environments, enabling organizations to maintain a strong security posture while adhering to regulatory requirements in real-time.
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring
Real-time compliance monitoring continuously assesses cloud environments against PCI DSS, HIPAA, NIST, and GDPR standards. Predefined templates enable automated checks, significantly reducing the time and effort required to maintain regulatory adherence.
If a compliance violation occurs, such as a HIPAA-compliant system’s misconfigured access control, the platform flags it immediately and initiates a remediation workflow. This proactive approach minimizes non-compliance risk and helps safeguard sensitive information across multi-cloud environments.
Risk Scoring and Prioritization
IBM Security and Compliance Center uses advanced risk scoring to manage security risks effectively. It assesses vulnerabilities by severity, business impact, and likelihood, helping teams prioritize their responses.
For example, a critical vulnerability in a public-facing server with high business impact may be prioritized over a low-severity misconfiguration in a non-production environment. This risk-based approach allows security teams to efficiently allocate resources to the most pressing issues.
The risk-scoring capabilities extend across AWS, Azure, IBM Cloud, and on-premises infrastructure, offering a holistic view of risks. The solution helps organizations streamline operations and avoid regulatory penalties by aligning risk management efforts with compliance obligations.
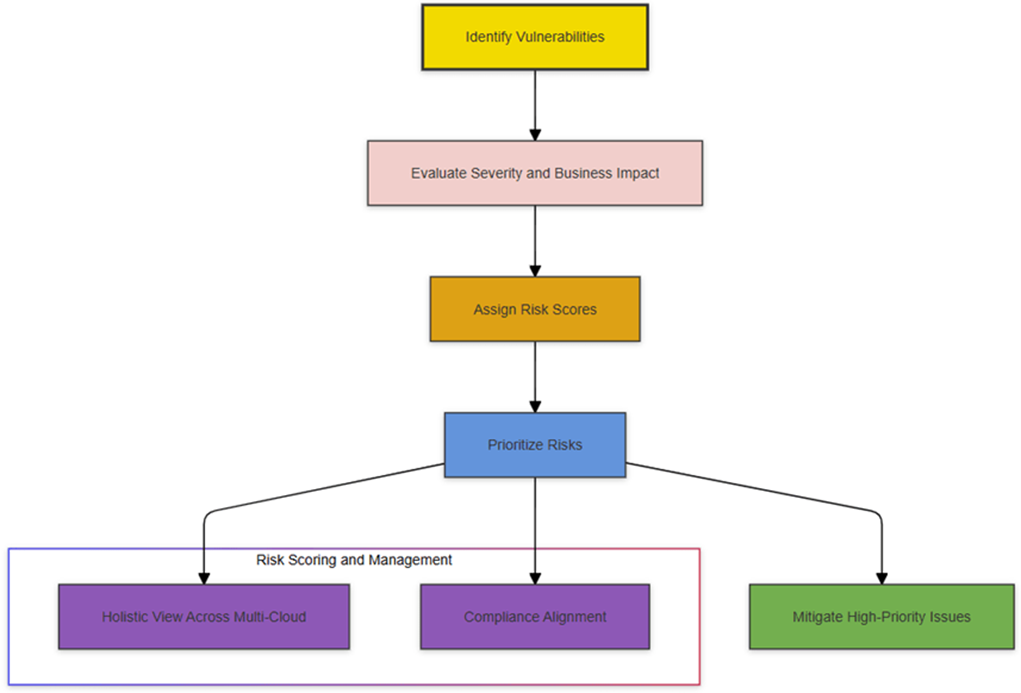
Figure 9 presents IBM SCC’s comprehensive risk scoring and prioritization process. It illustrates the key stages: identifying vulnerabilities, evaluating severity and business impact, assigning risk scores, and prioritizing risks. This structured approach helps organizations effectively mitigate high-priority threats while ensuring compliance alignment and maintaining a holistic multi-cloud security perspective.
Threat Detection and Response Across Clouds
IBM Security and Compliance Center offers a comprehensive approach to threat detection and response across multi-cloud and hybrid environments, integrating advanced analytics and automated response workflows to ensure effective risk management.
Advanced Analytics for Threat Hunting
The platform enables proactive threat hunting across cloud environments using machine learning and behavioral analytics. It correlates data from multiple sources, such as logs, container events, and network traffic, to identify patterns indicative of attacks.
For example, unusual network traffic from a container communicating with an unfamiliar external IP address may be flagged for further investigation to determine if a threat actor is attempting to exploit the container.
The solution monitors containerized workloads, Kubernetes clusters, and serverless functions, ensuring that suspicious changes are promptly investigated.
Automated Incident Response Workflows
Automated incident response workflows can be customized to an organization’s security policies. The platform can trigger automatic remediation actions when a threat is detected, such as quarantining compromised workloads or initiating forensic analysis. This automation reduces manual intervention, allowing security teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) capabilities also enable real-time monitoring of suspicious activities across multiple cloud environments, leveraging cloud-native insights to drive rapid detection and remediation. Integration with platforms like ServiceNow ensures that alerts include detailed insights, enabling swift response and minimizing downtime.
Automated response capabilities extend across multi-cloud infrastructures, ensuring consistent mitigation strategies for detected threats. For example, upon detecting suspicious activity in an AWS environment, the solution can initiate a predefined response action, notify the security team, and update related ticketing systems—all in real-time.
By combining advanced analytics with automated incident response, the IBM Security and Compliance Center helps organizations minimize the risk of data breaches and operational disruptions while maintaining regulatory compliance.
DevSecOps Integration and Cloud-Native Security
The platform is crucial in integrating security into the DevOps pipeline, ensuring security is embedded throughout the development lifecycle—commonly known as DevSecOps. This ensures that cloud-native applications are secure without sacrificing agility and speed of development.
Securing CI/CD Pipelines
Integration with CI/CD pipelines allows security checks to be automated early in development. This shift-left approach allows vulnerabilities and misconfigurations to be identified and resolved before workloads are deployed into production.
The solution provides continuous monitoring and protection across different CI/CD stages:
- Code Repositories: This tool scans code repositories for embedded secrets, vulnerabilities, and policy violations, helping developers catch and fix security issues early.
- Build Process: During the build phase, vulnerability scanning is conducted on container images and application dependencies to ensure that only secure components are used.
- Deployment: Checks for misconfigurations and compliance violations before deployment, ensuring that workloads meet security and regulatory requirements.
- Runtime: It provides real-time application monitoring, identifying and mitigating potential threats once deployed.
By automating security checks across CI/CD pipelines, the platform ensures consistent policy application, reducing the risk of human error and improving overall security.
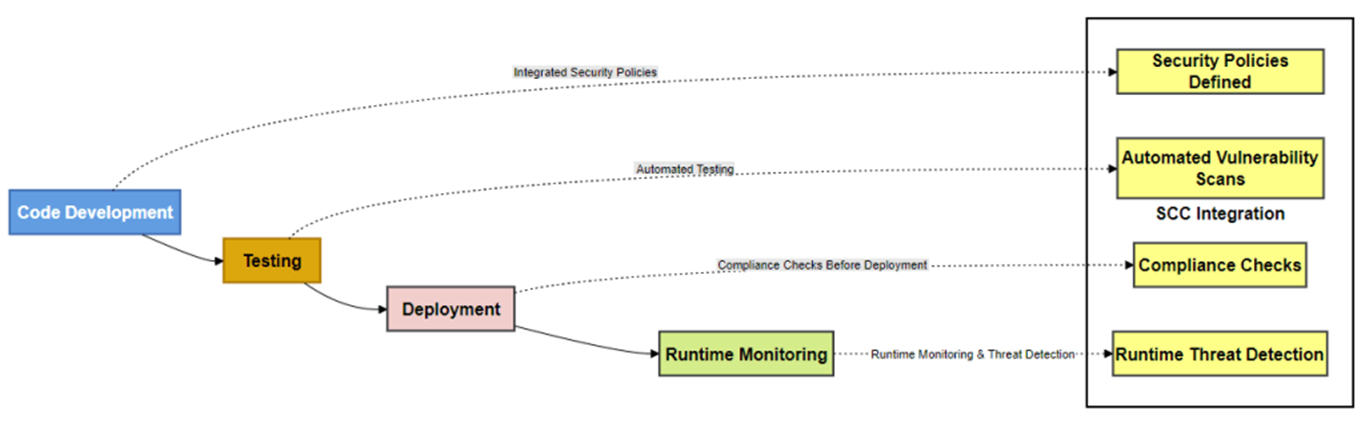
Figure 10 demonstrates how IBM SCC integrates seamlessly into the CI/CD pipeline, embedding security measures across key stages—development, testing, deployment, and monitoring. Ensuring security policies, automated vulnerability scans, compliance checks, and runtime threat detection are incorporated throughout the process, SCC enables agile, secure application development and achieves regulatory compliance.
Runtime Protection for Cloud-Native Applications
IBM Security and Compliance Center provides comprehensive runtime protection for cloud-native applications, ensuring consistent security across dynamic environments like containers, Kubernetes clusters, and serverless functions.
Key features of runtime protection include:
- Container Security: Monitors container behavior in real-time, preventing unauthorized activities such as unexpected process executions or anomalous network connections. This ensures containers operate with appropriate security configurations.
- Kubernetes Security: Continuously monitors Kubernetes clusters, ensuring secure access controls, network policies, and compliance with pod security standards. It also manages Kubernetes secrets, reducing the risk of exposure.
- Serverless Function Protection: Extends security to serverless functions, monitoring their execution to detect potential threats or anomalies.
- Behavioral Analysis: This tool leverages machine learning to establish baseline behaviors for cloud-native applications. Deviations from this baseline are flagged, enabling security teams to respond quickly to potential incidents.
- Automated Incident Response: When threats are detected, automated actions can be taken, such as isolating compromised containers or revoking credentials, to minimize the impact of security incidents.
These capabilities ensure consistent security for cloud-native applications across all deployment environments, maintaining a strong security posture regardless of workload location.
Continuous Compliance and Real-Time Risk Management
IBM Security and Compliance Center empowers organizations to maintain continuous compliance and manage risks effectively across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. The platform’s automated compliance checks and real-time monitoring ensure that organizations adhere to regulatory frameworks while avoiding emerging threats.
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring
The compliance monitoring capabilities continuously assess cloud environments against regulatory standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and NIST. Automated compliance checks leverage predefined templates, spanning cloud-native and traditional workloads, significantly reducing the manual effort required.
For example, if a HIPAA-compliant system experiences misconfiguration, the platform will flag it in real time, initiate remediation, and provide a detailed audit trail for compliance. This helps reduce the risk of regulatory penalties and maintains the security and privacy of sensitive information.
Risk Scoring and Prioritization
The platform incorporates advanced risk scoring and prioritization mechanisms to help organizations manage security risks effectively. By evaluating vulnerability severity, business impact, and exploitation potential, risk scores are assigned to guide teams on which threats to address first.
This risk-based approach ensures that high-priority issues—such as vulnerabilities in public-facing systems—are resolved quickly. The unified view across AWS, Azure, IBM Cloud, and on-premises infrastructure helps align risk management efforts with compliance obligations, reducing the likelihood of non-compliance and improving overall security.
Figure 5 illustrates the risk scoring and prioritization process within IBM SCC, highlighting the holistic capabilities of SCC’s Unified Dashboard. The flowchart outlines steps from identifying vulnerabilities to assigning risk scores, prioritizing remediation efforts, and providing comprehensive oversight into compliance, security alerts, workload protection, and data security—centralized for efficient management of high-priority risks in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
IBM Security and Compliance Center in Action: Case Study
Financial Services Case Study: Enhancing Cloud Security
A leading financial services client faced significant challenges managing security across multiple cloud platforms. These challenges included:
- Complex Regulatory Controls: The organization must adhere to stringent regulations across on-premises and cloud environments, including NIST and PCI DSS.
- Data Encryption and Key Management: Consistent key management and data encryption were necessary to meet internal security standards and regulatory compliance.
- Handling Misconfigurations: Misconfigurations across cloud platforms led to vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of non-compliance and potential data breaches.
Results with IBM Security and Compliance Center: The client achieved a 30% reduction in compliance costs, consistent enforcement of 97% of banking controls, and centralized configuration management, enhancing visibility and security across hybrid infrastructures.
This case study highlights how the platform helps organizations in highly regulated sectors streamline compliance, improve their security posture, and manage risks across diverse cloud environments.
Threat Detection and Response: Leveraging Advanced Analytics
The platform offers advanced threat detection capabilities, leveraging machine learning and behavioral analytics to identify and respond to risks across cloud infrastructures.
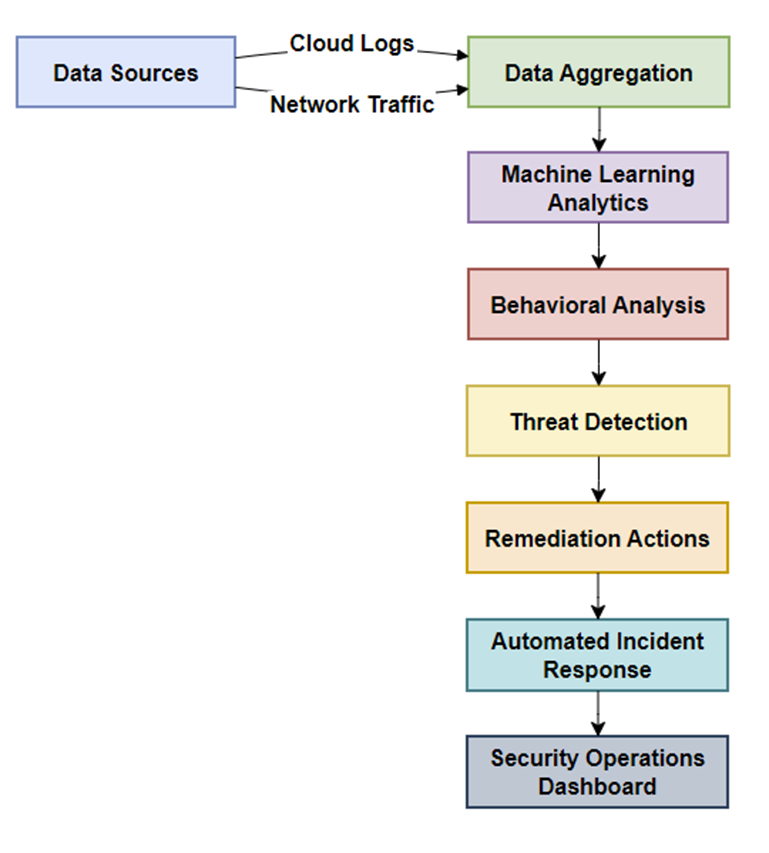
Figure 11: Threat Detection and Response Mechanism illustrates the threat detection and response stages in IBM SCC. Data sources such as cloud logs and network traffic are aggregated and analyzed using machine learning and behavioral analysis. Detected threats lead to automated incident responses and subsequent remediation actions displayed on the security operations dashboard.
Advanced Threat Detection and Hunting
The platform integrates threat-hunting capabilities by analyzing cloud events, network traffic, and container behavior to identify potential security threats. For instance, it can detect abnormal behavior, such as unexpected data exfiltration attempts from a containerized workload.
It helps security teams identify attack vectors that could otherwise remain hidden by correlating data across various cloud platforms.
Automated Response and Forensics
When threats are detected, automated response workflows are initiated, quarantining compromised workloads, terminating malicious processes, or launching forensic investigations. This automation helps ensure incidents are managed quickly and effectively, reducing manual intervention and mitigating risks.
The platform integrates with tools like ServiceNow, ensuring security teams receive timely alerts and recommendations for remediation actions, allowing them to make informed decisions swiftly.
Integration with DevSecOps
The platform integrates seamlessly with DevSecOps practices, embedding security throughout the CI/CD pipeline to ensure that all cloud-native applications are secure from development to production.
Shift-Left Security in CI/CD Pipelines
By embedding security checks early in the development lifecycle, the platform enables security teams to shift left, catching potential issues during coding and building rather than waiting until deployment. This helps minimize the vulnerabilities that reach production environments, ensuring secure application development.
Runtime Protection for Kubernetes and Containers
The platform provides runtime protection for Kubernetes clusters and containerized applications, monitoring suspicious behavior and ensuring compliance with security standards. Automated response capabilities help mitigate potential threats, such as container escapes or unauthorized resource access.
This integration ensures continuous security throughout the application development cycle, reducing the risk of breaches and maintaining adherence to compliance standards.
Conclusion
IBM Security and Compliance Center centralizes security management across multi-cloud and hybrid environments. With risk management, compliance automation, and advanced threat detection capabilities, it helps organizations maintain a resilient security posture across diverse cloud infrastructures.
The platform empowers businesses to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and meet regulatory requirements through real-time monitoring, analytics, and automated response workflows. Its seamless integration into DevSecOps ensures that security is embedded across every development lifecycle stage, from code to runtime.
As multi-cloud strategies become the norm, the IBM Security and Compliance Center is poised to play a crucial role in safeguarding digital assets, optimizing security processes, and ensuring operational continuity in an ever-evolving cloud landscape.
FAQs
What does SCC stand for in IBM’s context?
IBM Security and Compliance Center (SCC) is a comprehensive platform designed to establish policies, enforce security controls, and evaluate security and compliance across hybrid multi-cloud environments.
How does a multi-cloud environment differ from a hybrid cloud environment?
A multi-cloud environment leverages multiple public cloud providers for efficiency and innovation, while a hybrid cloud environment integrates on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources for greater data control.
What are the main security challenges associated with hybrid cloud models?
Key challenges include vendor compatibility, secure network integration, API management, data protection, visibility, and regulatory compliance.
What are the best practices for managing security in a hybrid cloud environment?
Effective management includes encrypting data, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, applying security patches, and enforcing a zero-trust model.
References
- KuppingerCole Analysts. (2023). Achieving Security and Compliance in Multi-Cloud Environments: IBM Security and Compliance Center Overview. Retrieved from https://www.kuppingercole.com/watch/achieving-security-compliance
- IBM. (2023). IBM Security and Compliance Center: Centralized Security and Compliance for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/products/security-and-compliance-center
- IBM. (2023). Key Features of Cloud Workload Protection in IBM Cloud Security and Compliance Center. IBM Cloud Documentation. Retrieved from https://cloud.ibm.com/docs/workload-protection?topic=workload-protection-key-features
- IBM. (2023). IBM Security and Compliance Center Case Study: Ensuring Cloud Security and Compliance. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/case-studies/security-compliance-center
- IBM Media Center. (2023). IBM Security and Compliance Center: A CNAPP Solution Suite for Cloud Security. Retrieved from https://mediacenter.ibm.com/media/IBM+Security+and+Compliance+CenterA+CNAPP+solution+suite/1_qkscd3b8
- KuppingerCole Analysts. (2023). IBM Security and Compliance Center: Delivering Security and Compliance in Hybrid Multi-Cloud Environments. Retrieved from https://www.kuppingercole.com/research/ev81351/ibm-security-and-compliance-center