Purpose Statement:
- This review intends to provide professionals and students with a clear, actionable understanding of the NIST AI RMF 1.0. By breaking down its key aspects, guidelines, and recommendations into a practical and accessible format, it aims to empower readers to comprehend and effectively implement AI risk management strategies in their respective fields. Whether you are an AI practitioner, policymaker, or student stepping into AI, this review aims to offer professionals and students an accessible and practical insight into the NIST AI RMF 1.0.
Introduction
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) aims to guide companies in managing risks associated with AI systems and promote reliable, responsible AI development and application. It serves as a voluntary resource for businesses of all sizes and sectors to gradually enhance AI system trustworthiness.
Defining Artificial Intelligence
The AI RMF defines “artificial intelligence” as systems exhibiting intelligent behavior by assessing their environments and taking actions to achieve specific goals. It encompasses technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, enabling machines to mimic human intelligence.
Scope and Application
The AI RMF’s broad scope covers various AI technologies and applications. Being non-sector-specific and use-case-neutral, it applies across industries and adapts to the evolving AI landscape.
Risk Factors and Management
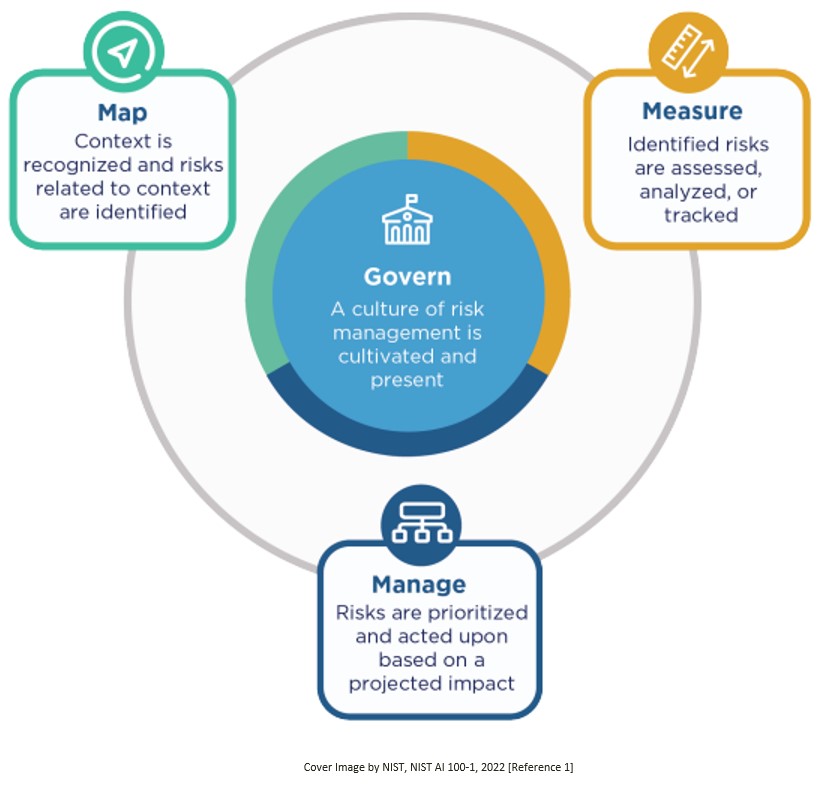
Risk factors in AI systems identified by the AI RMF include privacy, safety, security, explainability, accountability, transparency, validity, reliability, and fairness. The framework proposes a fourfold strategy for risk control—GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, and MANAGE. These strategies span the entire AI lifecycle, with specific functions and subcategories aiding enterprises in risk management.
Ethical Considerations in AI
The AI RMF emphasizes the creation of ethical AI, focusing on bias management, privacy protection, accountability, fairness, and transparency. It urges consideration of societal impacts and ethical implications in AI system development and deployment.
Addressing Bias and Fairness
Managing harmful biases and ensuring fairness in AI decision-making are critical focal points. The framework advocates for AI systems that minimize unfair impacts or discrimination.
Data Governance
Data governance guidelines stress the importance of privacy, integrity, and quality. The AI RMF encourages data provenance, minimization, sharing, and protection practices, aligning with existing standards like the NIST Cybersecurity and Privacy Frameworks.
Privacy in AI Systems
The AI RMF recommends incorporating privacy-enhanced features into AI systems to address privacy concerns. The framework directs organizations to utilize standards like the NIST Privacy Framework to manage privacy risks effectively.
Transparency and Communication
The AI RMF stresses the importance of using clear, accessible language to communicate AI risks to a broad audience. It promotes transparency in AI systems, urging organizations to provide stakeholders with relevant information and explanations of AI decisions.
Accountability in AI Development
The framework emphasizes organizational responsibility in AI system design, development, deployment, and usage. It advocates for governance protocols that ensure accountability, traceability, and oversight throughout the AI lifecycle.
Human Oversight in AI Systems
The framework emphasizes the crucial role of human judgment and decision-making in AI system development. The AI RMF promotes human-AI collaboration, advocating for human monitoring and intervention to ensure ethically sound decisions.
Security Concerns and Strategies
The AI RMF integrates approaches from existing cybersecurity frameworks to address AI security issues. It encourages the adoption of standards and best practices for creating secure and resilient AI systems.
Mitigating Deployment Risks
The framework offers strategies for reducing deployment risks, including conducting risk assessments, implementing security controls, ensuring privacy protections, and addressing environmental impacts.
Environmental Considerations
The AI RMF emphasizes considering AI systems’ energy consumption and carbon emissions, advocating for sustainable practices and energy-efficient algorithms, and optimizing AI model training and deployment.
Developing Resilient AI Systems
Building resilient AI systems involves robustness, reliability, thorough testing, redundancy, and contingency planning to mitigate potential disruptions or failures.
Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration
The AI RMF underlines the need for diverse expertise in AI, urging collaboration among domain experts, ethicists, data scientists, policymakers, and privacy professionals.
Global AI Risks and Collaboration
The framework encourages international cooperation to address global AI risks, sharing best practices and guidelines for responsible AI development across borders while considering diverse legal and regulatory contexts.
Ethical Decision-Making
The AI RMF promotes ethical decision-making in AI, aligning AI systems with values like fairness, accountability, and respect for human rights and privacy. It urges organizations to contemplate the ethical and societal implications throughout AI’s lifecycle.
Stakeholder Communication and Transparency
Unambiguous communication about AI systems’ purposes, capabilities, limitations, and risks is essential. The AI RMF encourages proactive, transparent engagement with all stakeholders, fostering mutual respect and understanding.
Balancing Innovation and Risk
The framework advocates for a proactive, iterative approach to AI risk management, promoting responsible innovation and a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Training and Education in AI Risk Management
Increasing awareness of AI risks and best practices among decision-makers and practitioners is vital. The AI RMF recommends integrating AI risk management into educational programs and providing targeted training.
Addressing AI Uncertainty
The framework suggests risk assessments to manage AI’s unpredictability, considering uncertainty factors and developing robust monitoring and adaptation mechanisms.
AI in Sensitive Applications
The AI RMF provides:
- Guidelines for responsible AI use in sensitive areas like surveillance and decision-making.
- Stressing the need for fairness.
- Transparency.
- Human oversight.
Integrating AI with Emerging Technologies
The framework advises a holistic approach to managing risks associated with AI and other emerging technologies, emphasizing interdisciplinary collaboration and knowledge-sharing.
AI and Intellectual Property
The AI RMF underscores the importance of respecting intellectual property rights in AI development, advising organizations to operate within legal frameworks while ensuring transparency and fairness.
Engaging in International AI Governance
Participation in international AI governance involves staying informed about global standards and engaging in collaborative efforts to harmonize AI governance approaches.
Compliance Monitoring and Auditability
The AI RMF sets standards for accountability and transparency in AI systems, recommending audit trails, documentation, and monitoring procedures to ensure legal and ethical compliance.
Fostering Public Trust in AI
To build public trust, the AI RMF emphasizes resolving privacy issues, adhering to legal and ethical standards, and addressing public concerns through transparent and accountable AI practices.
Addressing Workforce Impacts
The AI RMF acknowledges AI’s potential impact on the workforce, recommending proactive strategies like reskilling and upskilling to help employees adapt and maintain employment.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operating within legal and regulatory frameworks is crucial. The AI RMF advises consultation with legal and compliance specialists to ensure adherence to pertinent regulations.
Performance Measurement in AI
Setting up metrics and indicators to evaluate AI system performance is recommended. The framework emphasizes the importance of transparency in reporting AI performance to stakeholders.
Lifecycle Management of AI Systems
The AI RMF guides systematic lifecycle management, including planning, development, testing, operation, and retirement, ensuring accountability and traceability.
Scalability in AI Systems
Considering scalability in AI system design is essential. The framework advises designing systems capable of handling increasing data, user interactions, and computational demands.
Public and Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging with the public and stakeholders throughout the AI system lifecycle is vital. The AI RMF encourages open communication, feedback solicitation, and diverse perspectives in decision-making.
Alignment with International Standards
The framework seeks alignment with international norms and practices, adapting to global standards and the evolving AI community’s input.
Sector-Specific Challenges
Addressing unique challenges in sectors like healthcare and transportation is crucial. The AI RMF guides industry-specific issues, emphasizing safety, security, and ethical decision-making.
Public-Private Collaboration
Collaboration between public and private sectors in AI risk management and sharing knowledge and best practices for a comprehensive approach is encouraged.
Continuous Improvement in AI
The AI RMF emphasizes the need for ongoing improvement, adapting to new risks, integrating new knowledge, and adhering to evolving standards.
Adapting to the Evolving AI Landscape
Staying informed about AI advancements and regularly updating risk management strategies are essential for handling the dynamic nature of AI.
Model Validation and Testing Guidelines
Consulting official AI RMF documentation and related resources is recommended for detailed guidelines on AI model validation and testing.
Educational and Training Initiatives
Developing expertise in AI risk management through educational and training programs is emphasized, promoting awareness of best practices and risk management methodologies.
Managing AI’s Uncertainty and Risks
Adopting a risk-based approach and enhancing risk awareness are crucial for managing AI’s unpredictability. Continuous monitoring, assessment, and adaptation are vital in addressing emerging risks.
Responsible AI Use in Sensitive Applications
The AI RMF guides ethical and responsible AI use in sensitive applications, emphasizing transparency, fairness, and human oversight.
Integrating AI with Other Technologies
Considering the risks and challenges of integrating AI with emerging technologies requires comprehensive risk assessments and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Intellectual Property in AI
Respecting intellectual property rights while ensuring transparency and fairness in AI development is vital in operating within legal frameworks.
Global AI Governance Participation
Engaging in global AI governance involves staying current with international standards and collaborating to harmonize AI governance approaches.
Ensuring Compliance in AI
The AI RMF recommends establishing compliance monitoring and auditability procedures, ensuring accountability and transparency in AI systems.
Building Public Trust in AI
Resolving privacy issues, adhering to legal and ethical standards, and addressing public concerns are crucial to fostering public trust in AI systems.
Conclusion:
- As we progress through the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, it becomes clear that responsibility in this realm is not a one-time effort but a continuous journey of learning and adaptation. The insights from this review of the NIST AI RMF 1.0 underscore the importance of implementing a practical and dynamic AI risk management framework. Such a framework is pivotal for fostering trust among stakeholders and ensuring that the development and application of AI technologies align with ethical standards and societal values. Embracing these principles will be crucial for harnessing the full potential of AI in a way that benefits society while mitigating inherent risks. Let this review act as both a guide and an initial stepping stone, fostering ongoing engagement and continuous refinement in our collective journey toward a deeper understanding and education in AI risk management.
Key Learnings:
- The Fourfold Strategy – GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, and MANAGE: This comprehensive strategy is essential for navigating the entire AI lifecycle. It underscores the importance of a structured approach in managing AI risks, where each stage, from governance to management, plays a critical role in ensuring the responsible development of AI systems.
- Importance of Privacy, Safety, and Fairness: These factors are fundamental in ethical AI development. Privacy ensures that personal data is protected, safety guarantees that AI systems do not harm users or the public, and fairness ensures that AI decisions are unbiased and equitable. Together, these factors form the bedrock of trust and reliability in AI applications.
Practical Examples:
- For example, a healthcare AI system that analyzes patient data for personalized treatment plans. In this context, actively applying practical data governance principles is essential. Implementing strict access controls and anonymization techniques minimizes privacy risks by preventing unauthorized exposure of patient data. Furthermore, regular audits of the AI algorithms can detect and mitigate inherent biases, ensuring that treatment recommendations are fair and unbiased. This approach ensures that the AI system adheres to privacy regulations and upholds the ethical standards of fairness and equity in patient care.
Reflections and Insights:
- The AI RMF’s emphasis on human oversight invites a reevaluation of our role in AI. As creators, it prompts us to consider what we can build and what we should build, blending technological innovation with ethical responsibility. As ‘responsible co-pilots,’ this oversight challenges us to remain actively engaged with AI systems, ensuring they augment rather than replace human judgment. This dual role underscores a partnership with AI, where technology enhances human capabilities without undermining our values or autonomy.
Questions for Consideration:
- How can AI risk management practices be effectively communicated and implemented across different departments in your organization?
- How can biases in AI systems be identified and mitigated in your specific industry or sector?
- What strategies can enhance the transparency and accountability of AI systems within your organization?
- What are the potential ethical implications of AI deployment in your field, and how can they be addressed?
- How can human oversight be integrated into the AI systems used in your organization to ensure ethical decision-making?
- How can you implement measures to protect privacy and ensure data security in AI applications specific to your business?
- How can your organization stay abreast of and adapt to the evolving legal and regulatory landscape surrounding AI?
- How can you use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of AI systems in your operations?
- How can cross-disciplinary collaboration be fostered in your organization to address complex AI challenges?
- How can your organization contribute to fostering public trust in AI technologies?
Further Resources:
- For detailed model validation and testing guidelines, consult the NIST AI RMF official documentation and the companion Playbook.
Feedback Invitation:
- I welcome your thoughts and experiences with the NIST AI RMF 1.0. Let’s share our perspectives and continue learning together about responsible AI development.
References:
[1] U.S. Department of Commerce. Figure 5 – AI RMF Core. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST 100-1: An Architectural Definition of the AI Risk Management Framework, September 2022, page 25. Accessed January 23, 2023, https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ai/NIST.AI.100-1.pdf. Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology, Laurie E. Locascio; Secretary of Commerce, Gina M. Raimondo.
[2] NIST 100-1: An Architectural Definition of the AI Risk Management Framework, September 2022, Accessed January 23, 2023, https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ai/NIST.AI.100-1.pdf. Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology, Laurie E. Locascio; Secretary of Commerce, Gina M. Raimondo.
[3] NIST AI RMF Playbook, Accessed January 23, 2023, https://airc.nist.gov/AI_RMF_Knowledge_Base/Playbook