BCC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=24913461
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The AI Systems Spectrum
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Understanding the Power of Computer Vision
- Exploring Robotics
- The Mechanics of Rule-Based Systems
- Machine Learning
- Generative AI Potential
- Ethical Considerations and Future Trends
- Conclusion
- References
1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative force in technology, revolutionizing various sectors with its capabilities. AI is the simulation of human Intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the different facets of AI, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, Robotics, Rule-Based Systems, Machine Learning, and Generative AI. Each of the following sections provides a brief overview of core components, applications, and significance of these AI branches, followed by a discussion on ethical considerations and future trends in AI.
2. The AI Systems Spectrum
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a variety of technologies that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human Intelligence. We can broadly categorize these into several branches, each with unique contributions and applications:

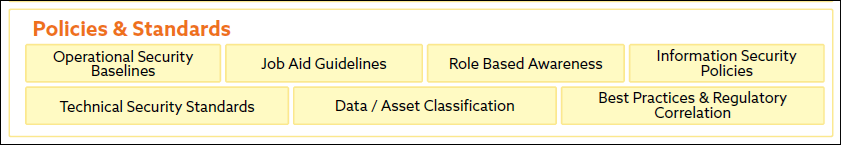
Overview
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is at the intersection of AI and linguistics, enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Applications include chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis, which enhance human-computer interaction and automate language-related tasks.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows machines to interpret visual data, which is essential for autonomous driving, medical imaging, and facial recognition. Computer Vision systems make decisions and perform tasks that require visual perception by understanding visual inputs.
Robotics
Robotics combines AI with physical machinery to create intelligent agents capable of performing complex tasks. Applications range from manufacturing robots to healthcare assistants, improving precision, efficiency, and adaptability in various fields.
Rule-Based Systems
Rule-based systems, including expert and fuzzy systems, rely on predefined rules for decision-making. They emulate human decision-making processes used in domains like medical diagnosis and industrial control.
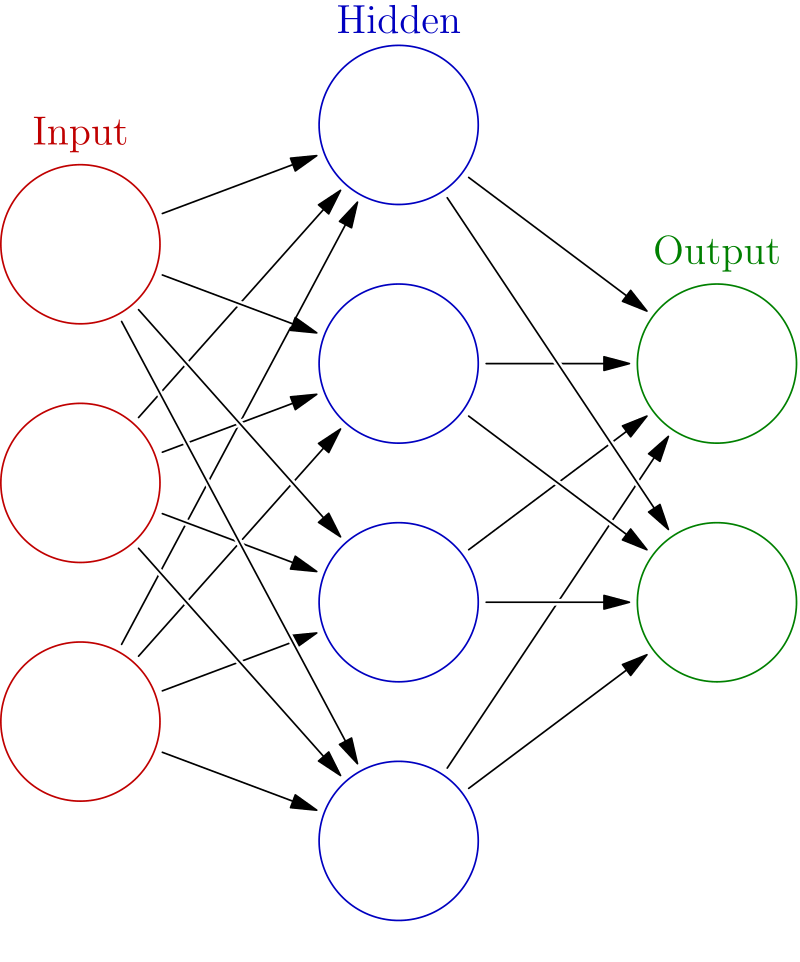
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) builds systems that learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming. ML is categorized into Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning, each with unique applications and methodologies.
Generative AI
Generative AI creates new data resembling existing data using advanced techniques like GANs and VAEs. It is pivotal in fields like image synthesis and text generation, pushing the boundaries of AI creativity and utility.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Overview
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. NLP powers various applications that impact our daily lives by enabling machines to understand and generate human language.
Text Classification
Text classification categorizes text into predefined classes, essential for spam detection, topic labeling, and sentiment analysis. Automating text categorization enhances data handling efficiency and accuracy.
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
NER identifies and classifies entities within the text, which is crucial for information extraction and context understanding. It is widely used in search engines and automated customer service to extract significant information.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis determines the sentiment expressed in text. It is valuable for understanding customer feedback and public opinion and for informing business decisions based on the emotional tone of content.
Machine Translation
Machine translation automates language translation, breaking down language barriers and enabling global communication. NLP advancements have improved translation accuracy and efficiency.
Question Answering
Question-answering systems provide accurate answers to natural language queries, enhancing virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. These systems rely on NLP to understand and retrieve relevant information.
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition converts spoken language into text, which is crucial for voice-activated applications and accessibility. NLP improves the accuracy and responsiveness of speech recognition systems.
Text Generation
Text generation creates coherent and contextually relevant text based on input. It is used in content creation and automated reporting. NLP-generated text assists in tasks requiring substantial written communication.
Real-World Example
GPT-x, an advanced NLP model, powers AI writing tools that generate human-like text, assisting in content creation and enhancing productivity in various fields.
4. Understanding the Power of Computer Vision
Overview
Computer Vision is a branch of AI that enables machines to interpret and act upon visual data. By mimicking the capabilities of human vision, Computer Vision has revolutionized numerous industries through applications such as image recognition, object detection, and video analysis.

Image Recognition
Image recognition identifies objects, people, places, and actions in images. It is fundamental in social media tagging, medical image analysis, and autonomous vehicles, enhancing visual data interpretation.
Object Detection
Object detection identifies and locates objects within an image. It is crucial for surveillance, autonomous driving, and robotics. It also improves situational awareness and decision-making.
Image Segmentation
Image segmentation partitions images into segments for detailed analysis. It is used in medical imaging, satellite imagery, and photo editing. It helps understand the structure and components of images.
Face Recognition
Face recognition identifies individuals based on facial features. It is used in security systems and social media tagging and provides authentication and identification.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR converts various documents into editable and searchable data, streamlining document digitization and processing. It automates data entry and text extraction from images.
Video Analysis
Video analysis processes video data to extract meaningful information. It is used in security, sports analytics, and entertainment and provides insights not easily discernible through manual observation.
Real-World Example
Tesla’s Autopilot uses object detection to identify and respond to road conditions, enhancing the safety and reliability of autonomous driving.
5. Exploring Robotics
Overview
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of AI that involves robot design, construction, operation, and use. Integrating various AI technologies, robotics aims to create machines capable of performing complex tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention.
Perception
Perception involves acquiring and interpreting sensory information, enabling robots to understand their environment. It is crucial for tasks like object recognition and navigation.
Motion Planning
Motion planning determines paths or movements for robots to achieve goals. It is essential for autonomous driving and robotic surgery. It ensures precise and safe robot movement.
Manipulation
Robotic manipulation involves interacting with objects, relying on advanced mechanical design for dexterity and precision. The manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare industries use it.
Control Systems
Control systems manage robot behavior, ensuring accurate task performance through real-time feedback. They maintain stability and responsiveness in robotic applications.
Localization
Localization determines a robot’s position within its environment, vital for navigation and task execution. Industries use techniques like GPS and SLAM for precise localization.
Human-Robot Interaction (HRI)
HRI focuses on communication between humans and robots, ensuring robots understand and respond to human instructions. It is crucial in service robotics and collaborative industrial robots.
Real-World Example
The da Vinci surgical system uses advanced robotic manipulation to assist surgeons in performing precise and minimally invasive surgeries, improving patient outcomes and recovery times.
6. The Mechanics of Rule-Based Systems
Overview
Rule-based systems are a fundamental aspect of AI. They are designed to mimic the decision-making abilities of human experts through a predefined set of rules. These systems play a crucial role in various applications where structured decision-making is essential.
Expert Systems
Expert Systems simulate expert judgment, using a knowledge base to solve specific problems. They provide decision support in fields like medical diagnosis and financial forecasting.
Fuzzy Systems
Fuzzy Systems use fuzzy logic to handle approximate reasoning and manage uncertainty in control systems. Applications like automatic transmission and climate control use them.
Inference Engines
Inference Engines apply logical rules to a knowledge base, deducing new information or making decisions. They are integral to Expert Systems and other AI applications requiring logical reasoning.
Production Systems
Production Systems use rules and a fact database to control actions. They are used in automated planning and scheduling and provide structured and efficient solutions for decision support.
Real-World Example
Fuzzy logic is used in washing machines to adjust wash cycles based on the load’s dirtiness, optimizing cleaning efficiency and resource usage.
7. Machine Learning
Overview
Machine Learning (ML) is a core subset of AI focused on building systems that can learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. We categorize ML into several paradigms: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Reinforcement Learning, and Generative AI.
Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the input-output pairs are known. The goal is to learn mapping from inputs to outputs, which data scientists and machine learning engineers can use to predict outputs for new inputs.
- Classification: For categorical outputs used in spam detection and image recognition.
- Regression: For continuous outputs, used in stock price prediction and weather forecasting.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning deals with data that does not have labeled outputs. The goal is to infer the natural structure within data points.
- Clustering: Market segmentation uses groups of similar data points.
- Association: Identifies relationships between variables used in market basket analysis.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Data visualization uses reduced variables.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) trains agents to make decisions by maximizing cumulative rewards.
- Q-Learning: Value-based method learning action values.
- SARSA: Similar to Q-Learning, but updates are made using actual actions taken.
- Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG): Combining deep learning and reinforcement learning for continuous action spaces.
Real-World Example
Netflix uses machine learning algorithms to recommend content to users based on their viewing history, enhancing user experience and engagement.
8. Generative AI’s Potential
Overview
Generative AI is a groundbreaking subset of AI focused on creating new data that mimics existing data. This area of AI has seen significant advancements, leading to the development of sophisticated models that can generate realistic images, texts, and even music.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs consist of two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator, trained simultaneously through a competition process. The generator creates data that tries to mimic the real data, while the discriminator evaluates the authenticity of the generated data.
- Generator Network: Produces data that resembles real data.
- Discriminator Network: Distinguishes between real and generated data, providing feedback to the generator.
Transformers
Transformers have revolutionized the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) with their ability to handle long-range dependencies in text. They use a mechanism called attention to weigh the importance of different parts of the input data.
- Attention Mechanism: Allows the model to focus on relevant parts of the input data.
- Encoder Layer: Processes the input data and creates a representation of it.
- Decoder Layer: Uses the encoder’s representation to generate the output data.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs are a type of autoencoder that generates new data by learning the latent variables of the input data. They work by encoding the input data into a compressed latent space and decoding it back to the original distribution.
- Encoder: Compresses the input data into a latent representation.
- Decoder: Reconstructs the data from the latent representation.
Diffusion Models
Diffusion Models generate new data by learning to reverse a diffusion process that adds noise to the data. This approach has generated impressive, high-quality images.
- Forward Process: Adds noise to the data incrementally.
- Reverse Process: Learns to remove the noise and reconstruct the original data.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs’ design focus is on sequential data handling, making them ideal for tasks involving time-series data or text.
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory): Handles long-term dependencies.
- GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit): Simpler and faster variant handling long-term dependencies.
Real-World Example
OpenAI’s DALL-E uses generative models to create images from textual descriptions, showcasing the creative potential of Generative AI.
9. Ethical Considerations and Future Trends
Overview
As AI becomes more prevalent, it is crucial to address potential ethical concerns and keep an eye on emerging trends that will shape the future of AI.
Ethical Considerations
Bias in Algorithms
AI systems can perpetuate existing biases present in training data, leading to unfair outcomes. Ensuring diversity in training data and implementing fairness checks are essential to mitigate bias.
Job Displacement
Automation through AI can lead to job losses in certain sectors, necessitating workforce retraining and adaptation. Preparing for these changes through education and policy can help ease transitions.
Privacy and Security
AI systems that handle sensitive data must ensure privacy and security measures to protect user information. Adopting best practices and regulations is critical for maintaining trust.
Future Trends
Explainable AI
Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make AI systems’ decisions understandable to humans, which is crucial for building trust and accountability. XAI techniques help users and regulators comprehend how AI models make decisions, increasing transparency.
Quantum Machine Learning
Quantum Machine Learning combines quantum computing with machine learning to solve complex problems more efficiently. This emerging field can potentially revolutionize cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery.
AI in Healthcare
AI is enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, and drug discovery. AI systems can identify patterns and provide insights that improve patient care and medical research by analyzing large datasets.
Real-World Example
Explainable AI aims to build trust in AI systems across various industries. For instance, XAI is becoming increasingly important for loan approval processes in the financial sector. Traditional credit scoring models often need more transparency, making it difficult for applicants to understand why lenders deny them credit. XAI-powered loan decision systems can explain the factors influencing the decision, such as income, debt-to-income ratio, and credit history, help the applicant understand the outcome, and allow lenders to ensure fairness and compliance with regulations.
10. Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a wide array of technologies that are transforming industries and enhancing our interaction with machines. From the structured decision-making of Rule-Based Systems to the creative potential of Generative AI, each branch of AI offers unique capabilities and applications. Understanding and leveraging these technologies can drive innovation and address complex challenges. Humanity must ensure technological progress is balanced with ethical implications and emerging trends to ensure AI development is beneficial and responsible.
Final Thought
As we enter a new era of AI, the challenge lies in harnessing its power to uplift humanity, tackle global issues, while safeguarding the inherent dignity of each individual.
11. References
- Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., … & Bengio, Y. (2014). Generative Adversarial Nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 27, 2672-2680. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generative_adversarial_network
- Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., … & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is All You Need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30, 5998-6008. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformer_(machine_learning_model)
- Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2014). Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. International Conference on Learning Representations. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoencoder#Variational_autoencoder_(VAE)
- Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., & Le, Q. V. (2014). Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 27, 3104-3112. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recurrent_neural_network
- LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep Learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436-444. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_learning