
Core Elements of Successful Security Program Management and Operations, Emphasizing the Need for a Multifaceted Approach to Strong Cybersecurity Posture
- Security Charter Creation:
- A guiding document defining the security team’s mission, scope, authority, and leadership.
- Aligns security goals with the organization’s overall objectives.
- Security Program Objectives:
- Focus on aligning security measures with core business processes.
- Prioritize risk management efforts by understanding your organization’s critical assets.
- Involve the entire workforce in security through training and awareness.
- Attack Surface and Risk Management:
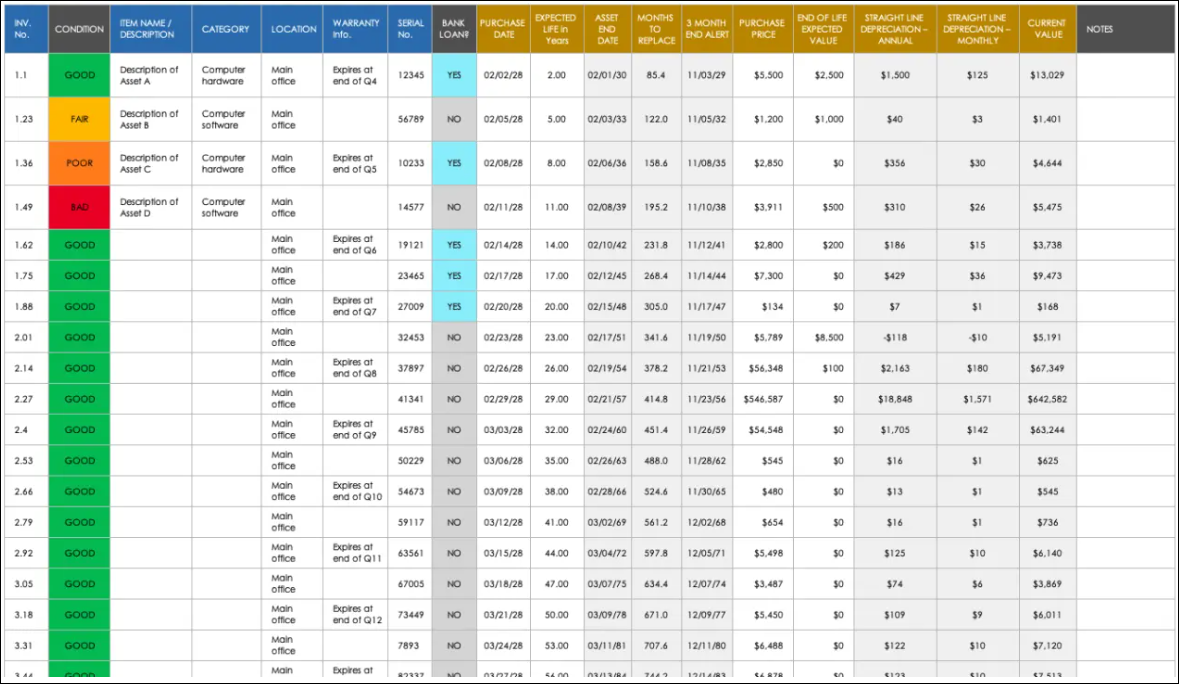
- Regularly updated asset inventory (all IT infrastructure, data, and systems) helps minimize the attack surface.
- Proactive risk assessments reveal vulnerabilities and help you manage them effectively.
- Compliance with industry regulations and legal requirements is crucial.
- IT asset inventory spreadsheet
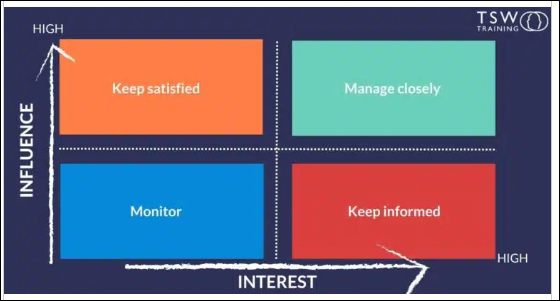
- Stakeholder Management:
- Identify decision-makers and individuals impacted by security initiatives.
- A stakeholder management plan helps maintain open communication and alignment.
- Cybersecurity Strategies:
- Develop adaptive strategies to counter evolving cyber threats.
- Prioritize high-risk assets and tailor defensive and offensive plans accordingly.
- Regular reviews and updates ensure your strategies stay effective.
- Implementation and Financial Management:
- Plan implementation carefully, set measurable goals, and adjust as needed.
- Financial planning determines budgets, spending, and investments in security measures.
- Security Budgeting and Cost Management:
- Estimate financial needs accurately and focus on areas that reduce overall risk.
- Balance financial constraints with smart security investments to optimize spending.
- Staffing and Resource Management:
- Ensure your security team has the right size and expertise to operate effectively.
- Understand industry staffing ratios and what motivates employees to improve retention.
- Professional Development and Morale:
- Foster an environment of learning and growth for security staff.
- Constructive feedback and recognition go a long way in building team morale.
- Security Program Architecture:
- Collaborate with stakeholders to gain broad support for security strategies.
- Roadmaps are important communication tools to outline short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals.
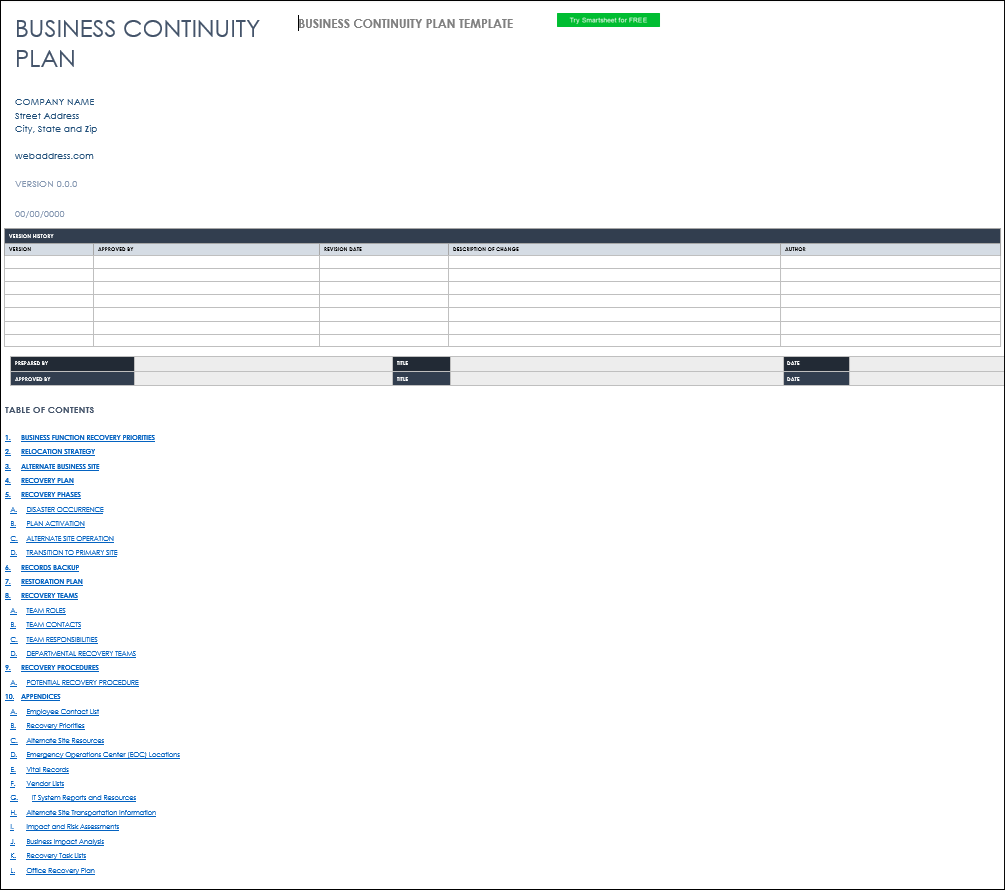
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
- Plans, simulations, and testing to ensure minimal disruptions from security incidents or unexpected events.
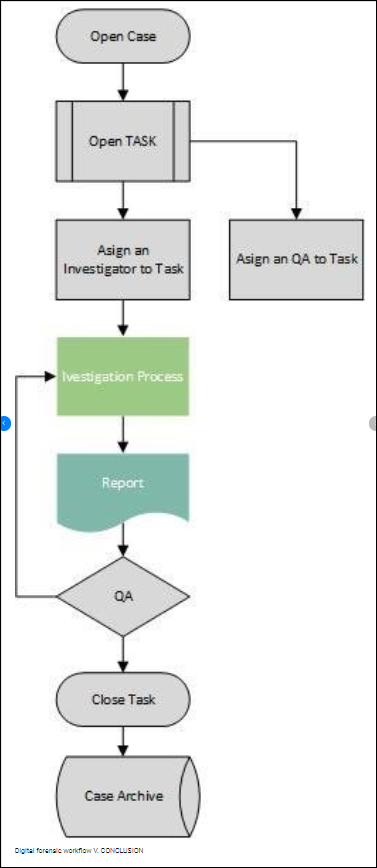
- Incident Response and Digital Forensics:
- Well-defined incident response plans handle security threats rapidly and effectively.
- Forensic analyses preserve evidence and identify root causes after a security incident.
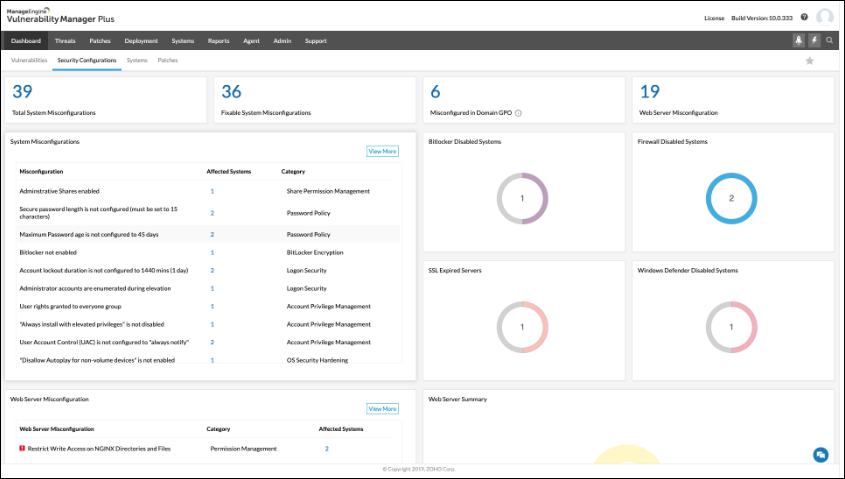
- Threat Management and Vulnerability Assessment:
- Proactive identification and prioritization of potential cyber threats.
- Vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and patch management help secure your systems.
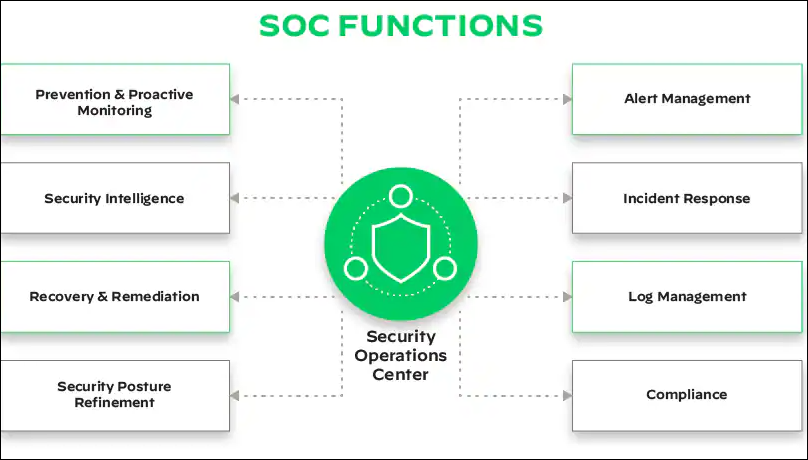
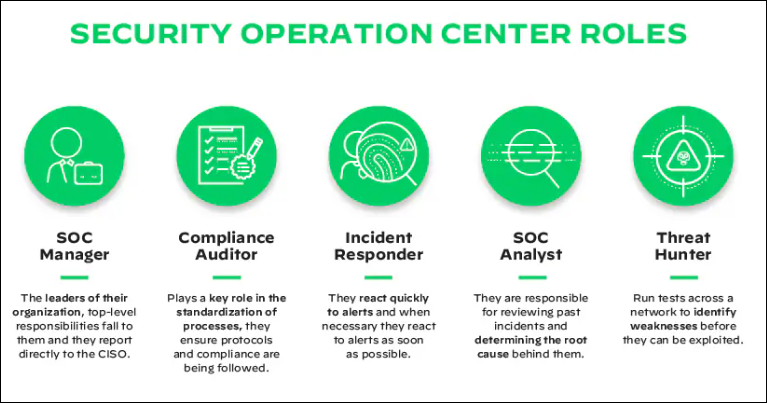
- Threat Hunting and Security Operations:
- A proactive approach to finding hidden threats in your systems.
- A Security Operations Center (SOC) is vital for centralized security monitoring and response.
Key Takeaway
- There must be more than isolated measures and tools to achieve a strong security posture. A comprehensive, well-designed program with integrated elements adaptive to the ever-changing threat landscape is essential in today’s complex digital world.
References
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27001:2022, Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection — Information Security Management Systems — Requirements. ISO, 2022.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27002:2022, Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection — Information Security Controls. ISO, 2022.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27005:2018, Information Technology — Security Techniques — Information Security Risk Management. ISO, 2018.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27032:2012, Information Technology — Security Techniques — Guidelines for Cybersecurity. ISO, 2012.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 31000:2018, Risk Management — Guidelines. ISO, 2018.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27035-1:2016, Information Technology — Security Techniques — Information Security Incident Management — Part 1: Principles of Incident Management. ISO, 2016.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27035-2:2016, Information Technology — Security Techniques — Information Security Incident Management — Part 2: Guidelines to Plan and Prepare for Incident Response. ISO, 2016.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 22301:2019, Security and Resilience — Business Continuity Management Systems — Requirements. ISO, 2019.
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 27031:2011, Information Technology — Security Techniques — Guidelines for Information and Communication Technology Readiness for Business Continuity. ISO, 2011.