Introduction
Imagine you want to describe a picture to a friend, but you can only use numbers. You might say, “The top left corner is bright, so that’s a 9. The bottom right is dark, so that’s a 2.” Using numbers to represent different parts of the picture creates a “vector” – a way for computers to understand and work with complex information like images or text.
What are Vector Databases?
A vector database functions like a big, organized library for these number-based descriptions:
- Storing: Like a library stores books, a vector database stores vectors—the number-based summaries of pictures or paragraphs.
- Finding Similarities: If you give the database a vector, it can quickly find other similar vectors. It’s like asking the librarian, “I liked this book. Can you recommend others like it?”
- Fast and Efficient: Vector databases are quick and can handle much information. They’re great for apps that need to make fast recommendations or find similar items.
Advanced Applications: Enhancing AI with Vector Databases, RAG, and Large Language Models
Now that we understand how vector databases facilitate fast and relevant retrievals let’s explore how these capabilities are instrumental in powering more complex AI systems, leading us to an advanced implementation where vector databases support and enhance AI capabilities in understanding and responding to human interactions.
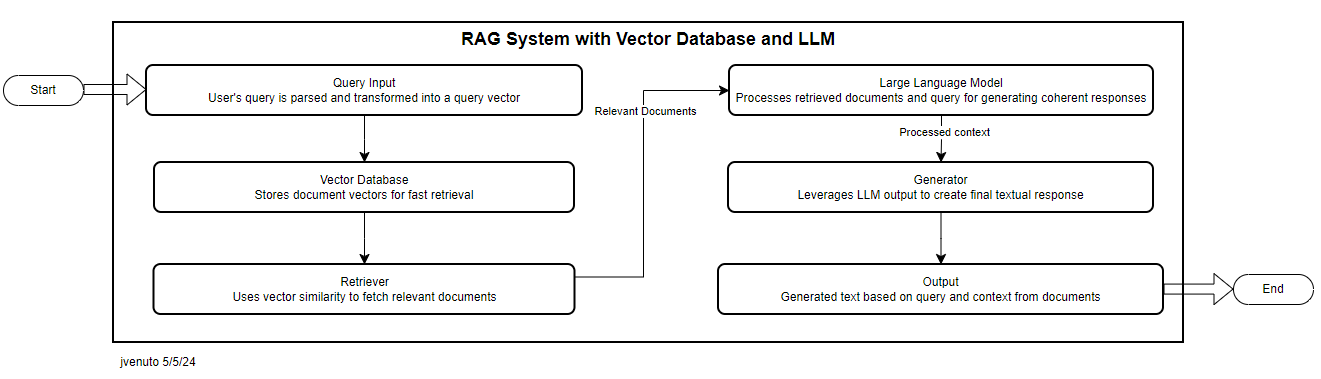
How Does a Vector Database Work with RAG and LLM?
The RAG model leverages the power of vector databases to improve the process of generating text-based answers. Here’s how it works in a simplified flow:
- Query Input: A user poses a question or input, and the system transforms it into a vector. This vector captures the semantic essence of the query.
- Vector Database Retrieval: The system uses the query vector to search through a vector database, quickly retrieving documents with semantically similar vectors.
- Use of Large Language Models: Once it fetches relevant documents, it processes them along with the original query. This model, trained on vast datasets, understands and synthesizes the information, producing context-rich, accurate responses.
- Generation and Output: The final step involves generating a coherent response that integrates the insights from the retrieved documents, effectively answering the user’s query.
The following diagram visually represents this flow:
Real-World Example: Why You Should Care
- Smarter Recommendations: How do online stores know exactly the type of shoes you’ll like? Or how do music services suggest artists you’ve never heard of but end up loving? That’s the power of vector databases!
- Finding the Perfect Match: Vector databases can help you find pictures that look similar to those you already have, even if they don’t have the same details, making searching for similar visuals much easier.
- More Relevant Searches: When you search for something like “healthy recipes,” a vector database can help you find truly relevant articles, not just ones that happen to contain those exact words, and no more endless scrolls through irrelevant results!
Popular Vector Databases
Here are several widely used vector databases:
- Faiss: Created by Facebook, it’s great for handling huge amounts of data, like what you might find in a social network.
- Milvus: An open-source option that offers flexibility and is usable across all applications.
- Pinecone: A user-friendly service that makes building apps with vector search capabilities easy.
- Annoy: Developed by Spotify, it recommends music and other media.
- Elasticsearch: Traditionally used for text search, but now has vector search capabilities, too.
- Weaviate: Another open-source option with handy features like automatic classification of data points.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, vector databases like Faiss, Milvus, and Pinecone are not just tools for managing data—they are at the heart of revolutionizing how machines understand and interact with the world. From powering simple app recommendations to driving sophisticated AI models that mimic human reasoning, vector databases are truly transforming our digital landscape.