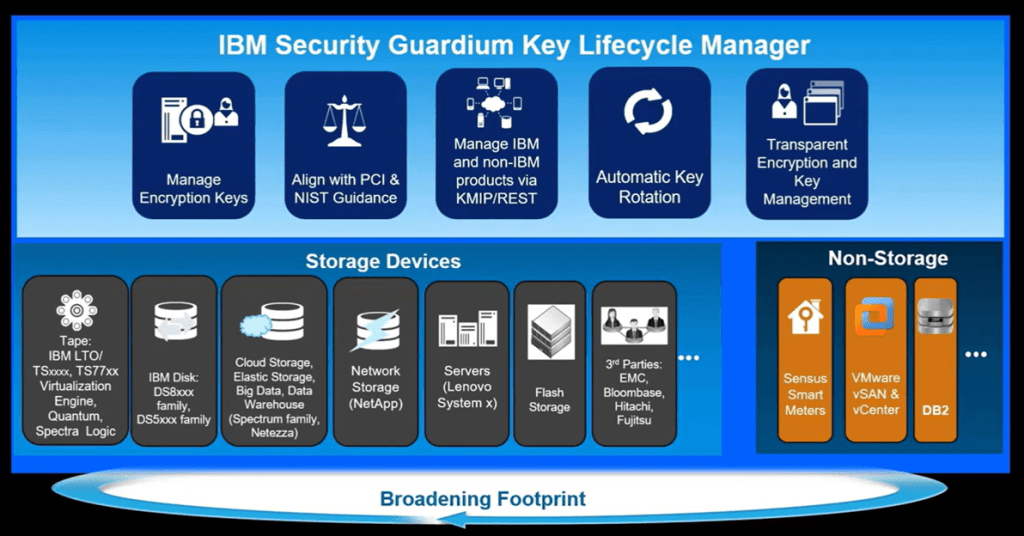
IBM Security Guardium Key Lifecycle Manager (GKLM) is a comprehensive solution designed to centralize, simplify, and strengthen the management of cryptographic keys throughout their entire lifecycle. Cryptographic keys are vital for securing data across various storage systems, applications, and cloud environments. They ensure data remains encrypted and only accessible to authorized users or systems. As organizations expand their digital footprints, the volume of keys and their complexity grow exponentially, making efficient key management a critical concern.
Executive Summary:
What GKLM Is: GKLM provides a comprehensive platform for the secure storage, management, and protection of cryptographic keys used in encrypting data. It supports multiple protocols, including Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP), and offers functionalities for key creation, distribution, rotation, and deletion, thereby automating and enforcing key management policies.
Why It’s Needed: Today, data breaches are a significant threat. Regulatory compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS mandate stringent data protection measures, including proper encryption key management. GKLM helps organizations:
- Meet these compliance requirements.
- Protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Automate and streamline the management of cryptographic keys, reducing operational overhead and minimizing human error.
- Enhance security by providing a centralized control point for managing keys across various environments.
Where GKLM Would Be Applied: GKLM’s versatility benefits various entities across various sectors and systems. Here’s perspective on who would typically apply GKLM:
- Financial Institutions: Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies can use GKLM to secure transaction data and safeguard customer information, ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals, clinics, and health insurance companies can implement GKLM to protect patient records and sensitive health data and adhere to healthcare compliance standards such as HIPAA.
- Retail Businesses: E-commerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and retail management systems can utilize GKLM to encrypt customers’ payment information and personal data, enhancing consumer trust and privacy.
- Cloud Service Providers: Companies offering cloud storage and services can deploy GKLM to manage encryption keys for customer data, providing secure and compliant cloud solutions.
- Enterprise IT Departments: Organizations with complex IT infrastructures, including data centers, virtual environments, and on-premise servers, can centralize their key management practices with GKLM, streamlining security protocols.
- Government and Defense Agencies: Entities dealing with classified and sensitive information can employ GKLM to meet stringent data protection requirements, ensuring national security and compliance with government regulations.
Any organization or entity managing encrypted data across various environments and facing regulatory compliance demands for data protection benefits from GKLM’s deployment. Its adoption spans sectors such as finance, healthcare, retail, technology, and government, addressing the critical need for secure and efficient cryptographic key lifecycle management.
The following is an abbreviated user guide for IBM Security Guardium Key Lifecycle Manager (GKLM):
- Introduction: GKLM provides centralized key management, secure storage, serving, and lifecycle management of cryptographic keys.
- System Requirements: Before installation, verify your system meets GKLM’s hardware and software prerequisites as detailed in the GKLM support matrix.
- Obtaining Installation Files: Download GKLM installation and license files from the IBM Passport Advantage website.
- License Activation File: Ensure you have the correct license file for your GKLM edition, which is crucial for activating the software post-installation.
- Choosing the Edition: Decide between Traditional and Container Edition based on your deployment environment. Traditional is suitable for standalone servers, while Container is for Red Hat OpenShift or Kubernetes environments.
- Installation Prerequisites for Traditional Edition: Check system prerequisites using the provided script in the installation package.
- Installing Traditional Edition: Run the launchpad.bat or launchpad.sh script and follow the wizard to install GKLM along with required IBM components like Db2 and WebSphere.
- Installing Container Edition: To deploy in a containerized environment, ensure Red Hat OpenShift or Kubernetes is set up and configured.
- Database Configuration: Configure the embedded Db2 database during installation for the Traditional Edition. For the Container Edition, prepare your PostgreSQL or Db2 database before deployment.
- Secure Communication Setup: Configure TLS/KMIP certificates for safe communication with encrypted devices and applications.
- Backup and Restore: Familiarize yourself with GKLM’s backup and restore functionalities to safeguard your cryptographic keys.
- LDAP Integration: Integrate GKLM with LDAP for centralized user management, leveraging existing organizational structures and permissions.
- Replication Configuration: Set up replication between two GKLM instances for redundancy and high availability.
- Deploying in Multi-Master Mode: Configure a Multi-Master cluster with multiple GKLM servers for environments requiring fault tolerance.
- Client Registration: Register self-encrypting devices and applications with GKLM to start managing cryptographic keys.
- Creating Cryptographic Keys: Utilize the GKLM GUI to create, import, or generate cryptographic keys for your applications and devices.
- Key Lifecycle Management: Learn how to manage key states (active, suspended, compromised, etc.) within GKLM for compliance and security.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Set up monitoring within GKLM to track key usage and system health. Configure alerts for critical events related to the key lifecycle.
- Applying Updates and Patches: Regularly update GKLM and its components to ensure your system is secure and running efficiently.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Familiarize yourself with common troubleshooting steps for key management, database connectivity, and replication issues.
- Security Best Practices: Follow IBM’s recommended security best practices for GKLM, including secure password policies and minimal privilege principles.
- Regular Maintenance Checks: Perform maintenance checks on GKLM to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Documenting Your Configuration: Keep detailed documentation of your GKLM configuration, including database settings, replication setups, and custom integrations.
- Engaging with IBM Support: Know how to engage IBM Support for troubleshooting and assistance, including providing necessary logs and system details.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about new GKLM features and best practices through IBM documentation, forums, and training resources.
Summary: This guide provides an overview of deploying and managing IBM Security Guardium Key Lifecycle Manager. These steps will help ensure a secure, efficient, and compliant key management environment.
References:
- https://www.ibm.com/mysupport/s/topic/0TO5000000025yUGAQ/key-lifecycle-manager
- https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/ibm-security-guardium-key-lifecycle-manager-support-matrix
- https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/ibm-security-guardium-key-lifecycle-manager-faqs
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=-jkv6R_Dgog