
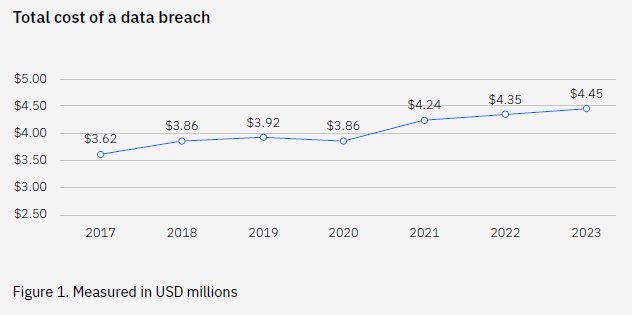
Security and data breaches can have devastating consequences, including financial loss, erosion of customer trust, and damage to reputation. According to the IBM 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach reached a record high of USD 4.45 million in 2023. A focused and tested action plan is essential for minimizing impact and ensuring rapid recovery. This article outlines such a plan, enriched with specific examples, technical depth, and actionable metrics.
I. Immediate Actions for Security and Data Breaches
When a breach occurs, the first response should focus on containing the incident and preventing further damage. Recommended immediate actions include:
- Isolating Affected Systems:
- Isolate systems where the breach occurred to prevent further loss or compromise. Allocate dedicated IT resources for this task.
- Activating Data Loss Prevention and Intrusion Prevention Systems:
- Activate DLP and IPS tools to contain the breach. Ensure these systems are updated and tested regularly.
- Assessing the Scope and Potential Impact:
- Understand the scope and potential impact of the breach, whether it’s data or security related. Use threat intelligence services for real-time analysis.
- Consulting Legal Counsel:
- Evaluate compliance with relevant laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA based on the type of breach. Prepare for potential legal actions and fines.
- Developing a Communication Strategy:
- Inform stakeholders, assessing the situation and legal obligations for breach notifications. Use a pre-defined communication template for efficiency.
II. Tools and Technologies for Security and Data Breach Protection
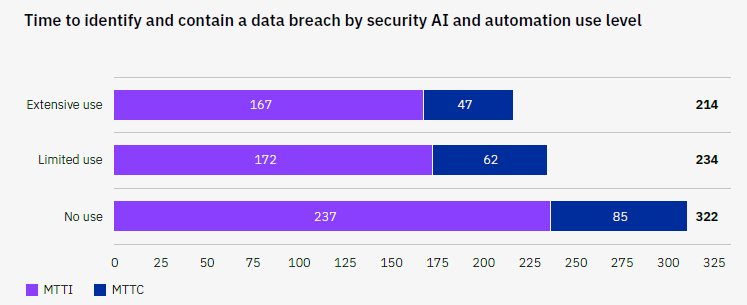
Organizations should implement robust security solutions as a preventative measure and respond effectively during a breach. According to the IBM 2023 report, organizations utilizing security AI and automation experienced a 108-day shorter time to identify and contain breaches, leading to USD 1.76 million lower data breach costs. Recommended technologies include:
- Data Encryption and Masking Solutions:
- Use AES-256 encryption to render stolen data unusable.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems:
- Implement solutions like Splunk or IBM QRadar for real-time threat analysis.
- Identity and Access Management Controls:
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect against unauthorized access.
- Firewalls, Intrusion Detection, and Prevention Systems:
- Employ next-gen firewalls and IDS/IPS like Palo Alto or Cisco.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software:
- Use solutions like McAfee or Norton to defend against malicious code.
- Backup and Recovery Systems:
- Implement cloud-based backup solutions for quick data recovery.
- Monitoring Systems:
- Use tools like Varonis to identify insider threats.
III. Ongoing Security and Data Protection Measures
In addition to incident response plans, companies need continuous security and data protection practices. According to the IBM 2023 report, only one-third of companies discovered the data breach through their own security teams, highlighting the need for improved threat detection capabilities.
Recommended practices include:
- Regular Risk Assessments and Penetration Testing:
- Conduct quarterly assessments and penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities proactively.
- Audits and Reviews of Data Practices:
- Perform bi-annual audits to uncover high-risk areas and ensure compliance.
- Security Awareness Training:
- Educate employees quarterly on best practices and emerging threats.
- Vendor Risk Management Programs:
- Assess and monitor third-party security risks through a dedicated vendor management platform.
- Data Recovery Strategies:
- Implement RAID configurations and cloud backups for availability assurance.
- Testing the Incident Response Plan:
- Conduct bi-annual drills and simulations using red team-blue team exercises to evaluate its effectiveness.
IV. Post-Mortem Analysis and Lessons Learned
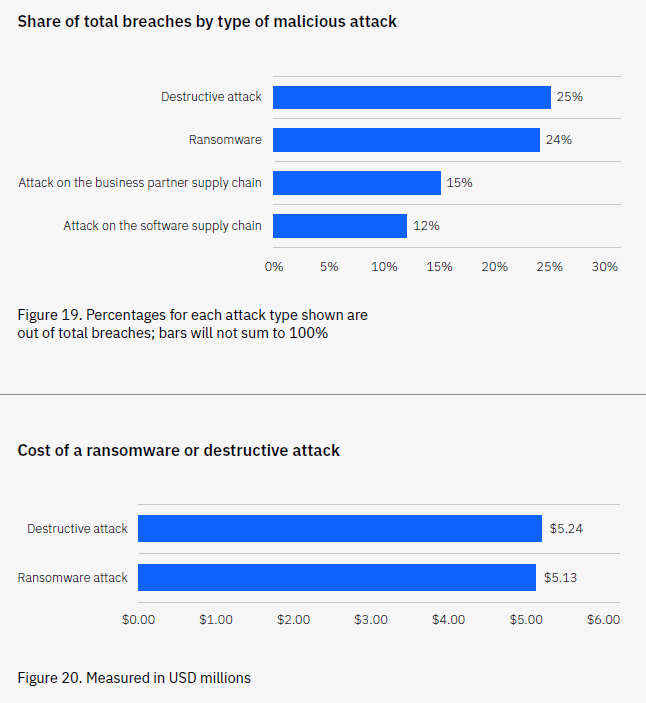
A detailed post-mortem analysis of the factors that led to a breach is crucial for improving security measures. According to the IBM 2023 report, ransomware attacks accounted for 24% of malicious attacks, with an average cost of USD 5.13 million. Key aspects of this process include:
- Assembling a Cross-Functional Response Team:
- Include IT, security, legal, and management. Assign an executive sponsor for oversight.
- Comprehensively Gathering Information:
- Collect data logs, user activities, and network traffic for a thorough analysis.
- Identifying Vulnerabilities and Holes in Defenses:
- Use tools like Wireshark and Nessus for deep analysis.
- Evaluating the Organization’s Response:
- Measure the time taken to detect and contain the breach as KPIs.
- Deriving Lessons and Developing an Action Plan:
- Use a SWOT analysis to identify gaps and improvement areas.
V. Prioritizing and Implementing Action Items
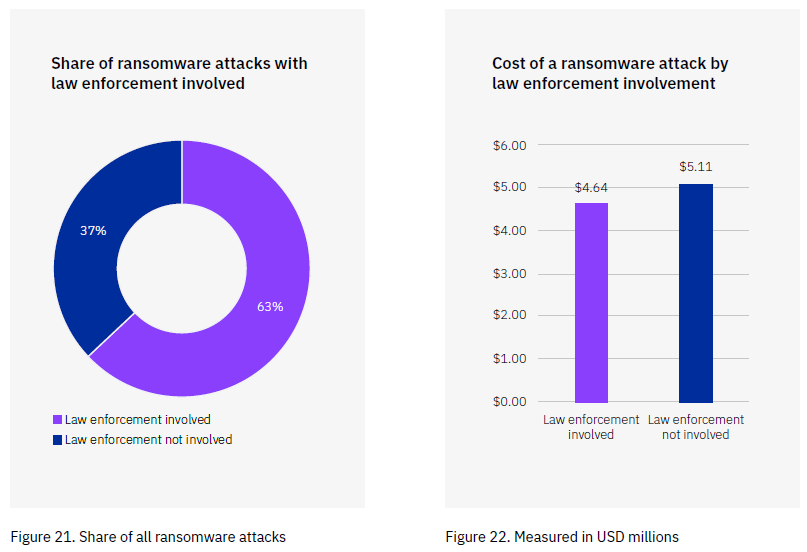
The remediation plan following a breach should focus on fixes that provide maximum risk reduction. According to the IBM 2023 report, involving law enforcement in ransomware attacks resulted in lower costs and shorter breach lifecycles. To achieve this, companies should:
- Prioritize Action Items:
- Use a risk matrix to prioritize based on severity, potential impact, feasibility, compliance impact, and urgency.
- Involve Stakeholders Early:
- Engage departments like HR, finance, and operations for a holistic approach.
- Engage Employees in Implementation:
- Use gamification techniques to encourage participation.
- Maintain Accountability:
- Use a centralized tracking system like Jira for action items.
VI. Communication, Reporting, and Stakeholder Management
Ongoing communication and transparency are vital during the breach response and post-breach phases. Best practices include:
- Regular Status Updates and Progress Reports:
- Use dashboards for real-time tracking.
- Upper Management Involvement:
- Obtain buy-in for resources, oversight, and expedited decision-making.
- Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Use tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for effective communication.
VII. Incentives, Recognition, and Continuous Improvement
To sustain momentum on security enhancement post-breach, companies should:
- Provide Incentives for Employees:
- Offer training programs or certifications for those who contribute to security improvements.
- Establish Recognition Programs:
- Use monthly or quarterly awards to highlight contributions.
- Define Metrics and KPIs:
- Use metrics like ‘Time to Detect’ and ‘Time to Respond’ as KPIs.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Update the action plan based on lessons learned, new risks identified during assessments, and evolving cyber threats.
Glossary
- GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation
- HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- CCPA: California Consumer Privacy Act
- AES-256: Advanced Encryption Standard (256-bit)
- SIEM: Security Information and Event Management
- MFA: Multi-Factor Authentication
- RAID: Redundant Array of Independent Disks
- SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
- KPI: Key Performance Indicator
References
- “The 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report,” IBM Security, 2023.
- “Data Breach Response Guide,” Experian, 2021.
- “GDPR Compliance: What Businesses Need to Know,” Harvard Business Review, 2018.
- “Cybersecurity Best Practices,” National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 2021.
In summary, being prepared with a focused and tested action plan is crucial for minimizing the damage from data breaches and accelerating recovery. Staying vigilant, making security enhancements a company-wide priority, and learning from incidents can help strengthen resilience against future attacks.
This concise guide aims to serve as a blueprint for organizations looking to fortify their security posture. With real-world examples, statistics, and actionable metrics, it provides a holistic view of how to navigate the complex landscape of data and security breaches.